Figure 1.
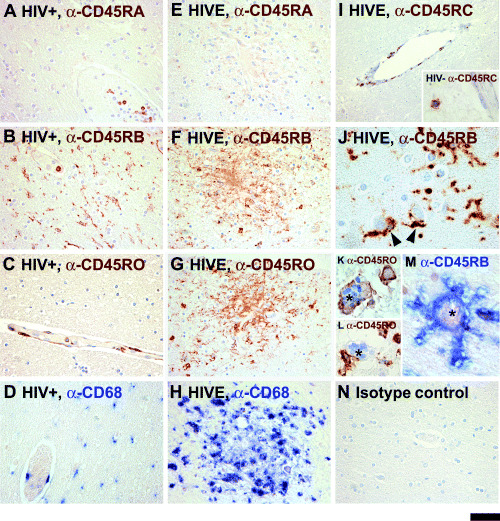
CD45 isoform expression in HIV encephalitis (HIVE) and control brains. Sections of the control and HIVE brains are immunostained with antibodies against CD45RA, RB, RC or RO as described in the Materials and methods. Results of the two non‐HIVE controls groups (HIV− and HIV+) are similar (also see 3, 2), but only HIV+ are shown here. Panels A–D show HIV‐seropositive brains stained with αRA, αRB, αRO and αCD68. Panels E–H show serial sections of an HIVE brain depicting a microglial nodule immunostained for CD45 isoforms and CD68. The αRA‐ and αRC‐reactive cells are mainly limited to leukocytes within the bloodstream with rare perivascular and/or parenchymal positive cells noted in both non‐HIVE and HIVE brains (A, E and I, also see Figure 2). αRB‐reactive cells are abundant in all brains and they include ramified microglial cells in HIV− (see Figure 5A) and HIV+ (B), as well as activated microglial cells within and outside the microglial nodules in HIVE (F and J). Multinucleated giant cells (MGCs) are also RB+ (asterisk, M). Panel J demonstrates a high power image of αRB‐reactive perineuronal microglia in the gray matter (arrowheads). αRO reactivity is detected in infiltrating lymphocytes, perivascular macrophages and microglial cells in HIVE (G), including MGCs (asterisk, K). Some MGCs are RO− (asterisk: L). Control brains show more limited RO staining (C and also see Figure 3E). Microglia and macrophages in non‐HIVE and HIVE brains are positive for CD68, a marker of brain macrophages (D and H). An HIV+ section treated with normal mouse IgG2a is shown as a control (N). Sections are counterstained with hematoxylin. The scale bar represents 50 µm in A–H and N, 100 µm in I and 20 µm in I inset and J–M.
