Figure 1. Methylation State-Specific Recognition of Histone H4-K20 by 53BP1 Tandem Tudor Domains.
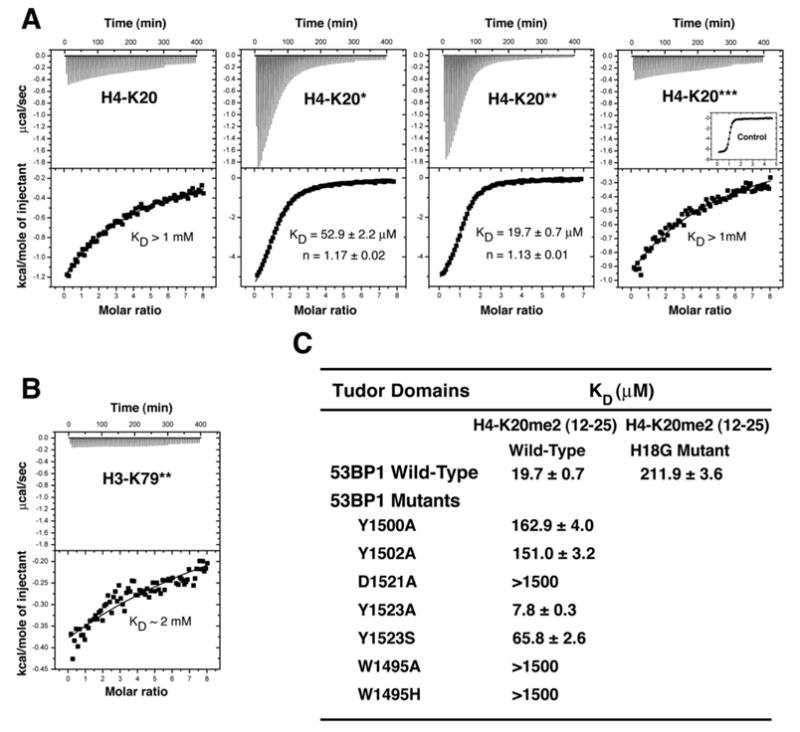
(A) Representative ITC results for the titration of 53BP1 tandem tudor domains with, from left to right panels, nonmethylated, monomethylated, dimethylated, and trimethylated H4-K20 (residues 12–25). The number of stars (★) indicates the number of methyl groups attached to Nζ of Lys20. Shown for each experiment are the integrated heat measurements from raw titration data as well as curve fitting with a standard one-site model. Inset in the last panel is a control titration of JMJD2A hybrid tudor domains with trimethylated H4-K20.
(B) ITC titration of 53BP1 with dimethylated H3-K79 (residues 74–83).
(C) Effects of point mutations in 53BP1 tandem tudor domains on the interaction with H4-K20me2. For each interaction, the dissociation constant (KD) derived by fitting a standard one-binding site model (Wiseman et al., 1989) is reported with the associated error determined by nonlinear least squares analysis.
