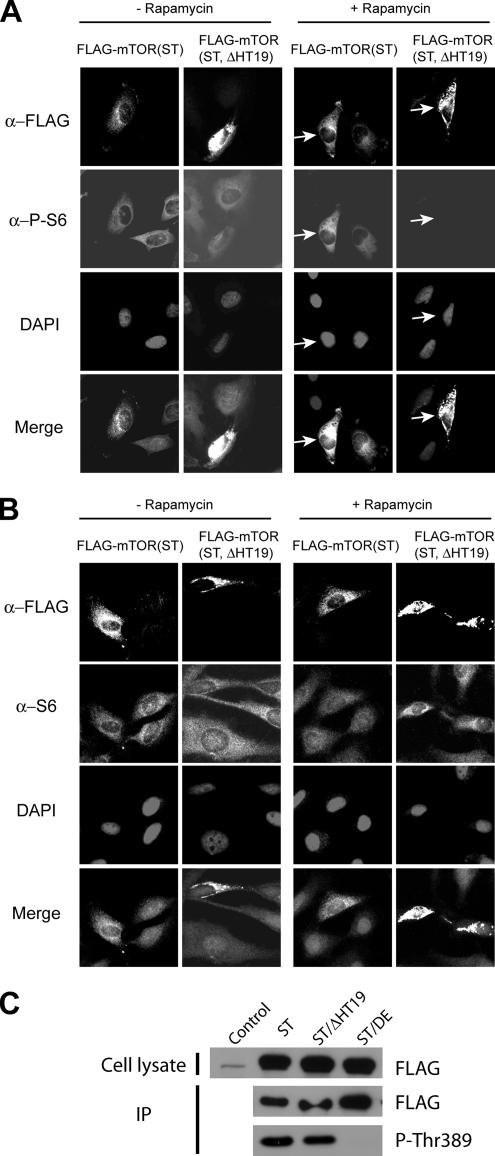
Figure 5.
Deletion of HT19 inhibits the ability of mTOR to promote S6 phosphorylation. (A) FLAG-mTOR(S2035T) and FLAG-mTOR (S2035T, ΔHT19) were transiently expressed in HeLa cells. These cells were then treated with the drug carrier (−Rap) or with rapamycin (+Rap) for 2 h and analyzed for the expression of FLAG-mTOR variants and S6 phosphorylation by IF staining with a FLAG antibody and a P-S6 antibody, respectively. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. The arrowheads indicate FLAG-mTOR(S2035T)– and FLAG-mTOR(S2035T, ΔHT19)–expressing cells. (B) Expression of FLAG-mTOR proteins does not affect S6 expression. This experiment is performed the same way as Figure 5A except a S6-specific antibody instead of the P-S6 antibody was used. (C) Deletion of HT19 does not affect mTOR kinase activity. FLAG-mTOR(S2035T), FLAG-mTOR(S2035T, ΔHT19) or FLAG-mTOR(S2035T, D2357E)(kinase-dead) were transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. After immunoprecipitation, they were assayed for mTOR kinase activity toward GST-p70S6K1(aa333-412). Thr389 phosphorylation was detected by Western blot with a P-Thr389 antibody.