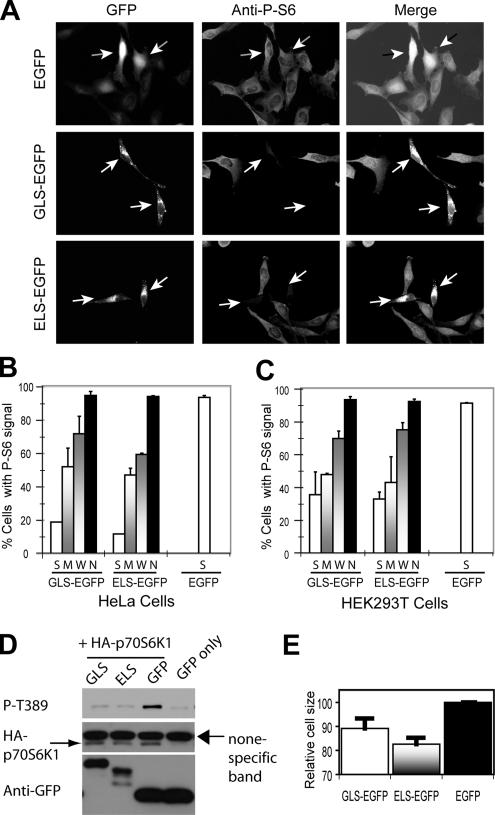
Figure 6.
Overexpression of GLS-EGFP and ELS-EGFP inhibits mTORC1. (A) Overexpression of GLS-EGFP and ELS-EGFP inhibits S6 phosphorylation in HeLa cells. EGFP, ELS-EGFP, and GLS-EGFP were transiently expressed in HeLa cells. S6 phosphorylation was determined by IF using a P-S6–specific antibody. The arrowheads indicate transfected cells. (B) Quantification of cells with P-S6 signal from the experiment in B. The expression level of EGFP fusion proteins in individual cells was categorized into S, M, W, and no (N) signal according to the GFP signals. Virtually all the cells expressing EGFP alone show strong GFP signal. (C) Overexpression of GLS-EGFP and ELS-EGFP inhibits S6 phosphorylation in HEK293T cells. EGFP, ELS-EGFP, and GLS-EGFP were transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. P-S6 signal was quantified and the level of GFP signal in individual cells was categorized as in Figure 6B. (D) Overexpression of GLS-EGFP and ELS-EGFP inhibits Thr389 phosphorylation of p70S6K1 in HEK293T cells. HA-p70S6K1 was transiently expressed in HEK293T cells together with ELS-EGFP, GLS-EGFP, or EGFP. HA-p70S6K1 phosphorylation was assayed by Western blot using a P-Thr389–specific antibody. (E) ELS-EGFP, GLS-EGFP, or EGFP was transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The size of EGFP-positive cells was measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorting.