Abstract
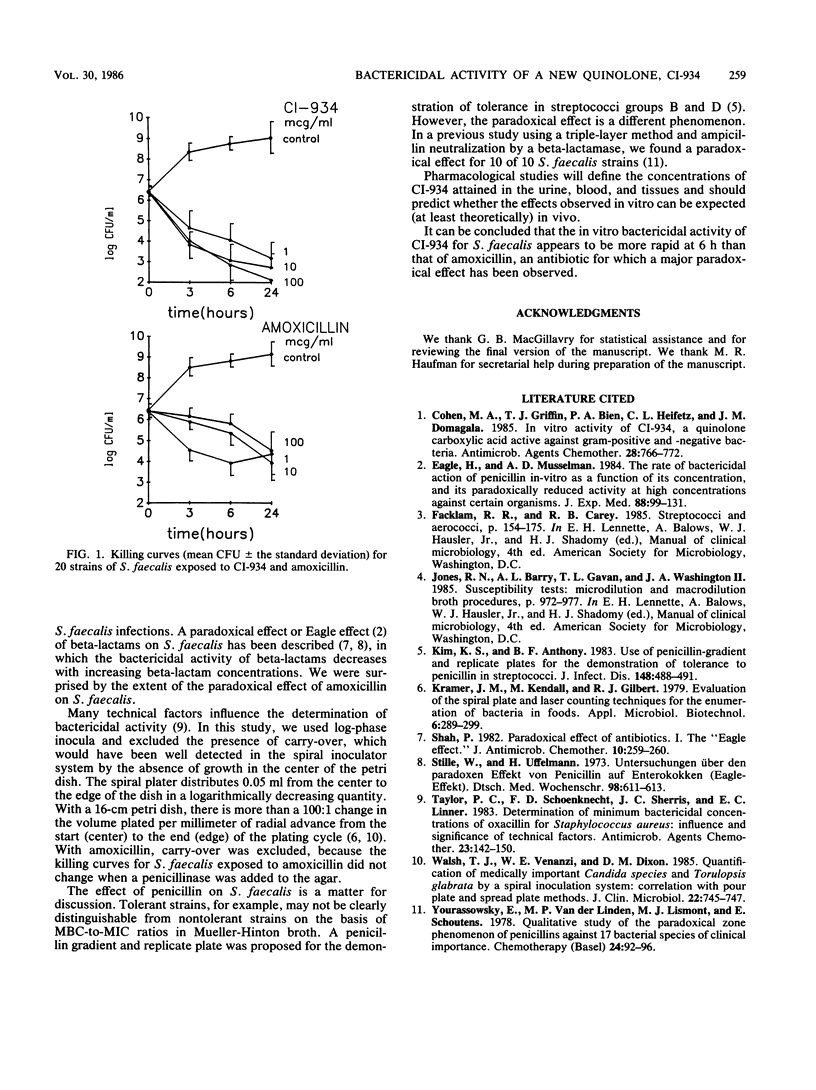
The rate of bactericidal activity of a new quinolone, CI-934, was compared with that of amoxicillin for 20 strains of Streptococcus faecalis. At 10 and 100 micrograms/ml, the bactericidal activity of CI-934 was more rapid at 6 h than that of amoxicillin. A paradoxical effect (a killing rate higher at 1 microgram/ml than at 100 micrograms/ml at 6 h) was observed for 19 of the 20 strains with amoxicillin and for 1 of the 20 strains with CI-934. It remains to be demonstrated whether in vivo studies will confirm the results obtained in vitro.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen M. A., Griffin T. J., Bien P. A., Heifetz C. L., Domagala J. M. In vitro activity of CI-934, a quinolone carboxylic acid active against gram-positive and -negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):766–772. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Anthony B. F. Use of penicillin-gradient and replicate plates for the demonstration of tolerance to penicillin in streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):488–491. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah P. M. Paradoxical effect of antibiotics. I. The 'Eagle effect'. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Oct;10(4):259–260. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.4.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stille W., Uffelmann H. Untersuchung über den paradoxen bakteriziden Effekt von Penicillinen auf Enterokokken (Eagle-Effekt. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1973 Mar 23;98(12):611–613. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. C., Schoenknecht F. D., Sherris J. C., Linner E. C. Determination of minimum bactericidal concentrations of oxacillin for Staphylococcus aureus: influence and significance of technical factors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. J., Venanzi W. E., Dixon D. M. Quantification of medically important Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata by a spiral inoculation system: correlation with pour plate and spread plate methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):745–747. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.745-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yourassowsky E., Vander Linden M. P., Lismont M. J., Schoutens E. Qualitative study of paradoxical zone phenomenon of penicillins against 17 bacterial species of clinical importance. Chemotherapy. 1978;24(2):92–96. doi: 10.1159/000237766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


