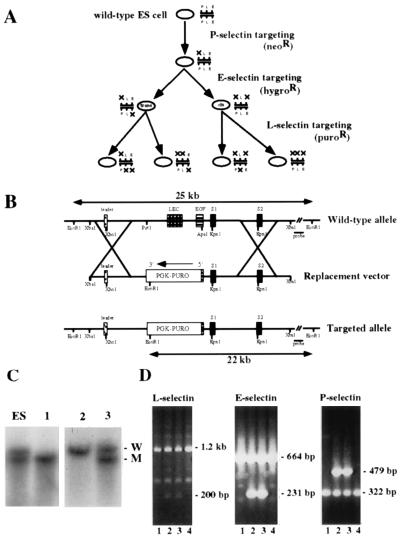
Figure 1.
Targeting strategy and L-selectin genotyping of progeny from double heterozygous crosses. (A) Overall scheme for generating mice deficient in one, two, or three selectins. P-, E-, and L-selectin loci were sequentially mutated by homologous recombination in ES cells by using replacement targeting constructs carrying drug-resistance genes for neomycin, hygromycin, and puromycin, respectively. By targeting the L-selectin locus in two different heterozygous ES cell clones with null mutations in P- and E-selectins, all possible combinations of heterozygous selectin-deficient ES cell clones were generated. Targeting of the P- and E-selectin loci has been described (2, 5). (B) The WT L-selectin locus is shown in the upper line. To construct the targeting vector, the PUROr cassette was inserted into 6.4 kb of L-selectin sequence. The exons encoding the lectin (LEC) domain and most of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) domain were deleted in this process. Resistant clones were screened with a 3′ probe that identifies the targeted 22-kb mutant and 25-kb WT bands upon EcoRI digestion. The XbaI–EcoRI fragment 3′ of the replacement vector is approximately 17 kb long; the XbaI–EcoRV probe comprises the first 1.6 kb of this segment. (C) Southern blot analyses of the L-selectin locus from EcoRI digests. Genomic DNA was extracted from tail biopsies of representative litters derived from mating heterozygous animals known to be carrying the L-selectin mutation. The first lane shows a digest of an ES cell clone, heterozygous for the L-selectin mutation, for comparison. W, WT allele; M, mutated allele. (D) PCR analysis of L-, E-, and P-selectins of progeny from an intercross of animals carrying heterozygous mutations in all three alleles. The targeted E-selectin band is 231 bp in length, the targeted L-selectin band is 200 bp in length, and the targeted P-selectin band is 479 bp in length. The null mutations segregate together during meiosis, indicating the mutations exist in cis. Null progeny from two such crosses were used to establish a homozygous triple-deficient line.