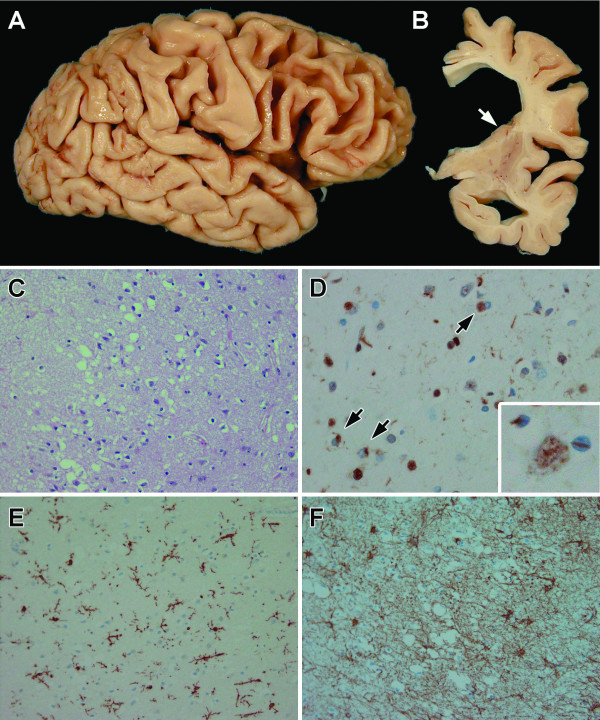
Figure 4.
Neuropathology of FTLD-U with PGRN mutations. Gross cortical atrophy is visible in frontal and superior temporal lobes (A). In coronal sections (B), the lateral ventricle is dilated and the caudate nucleus is flat (arrow). Laminar spongiosis in the layer II of the cortical ribbon (C) is associated with TDP-43-positive neuronal cytoplasmic (D, arrows) and "lentiform" intranuclear inclusions (inset). Severe neuronal loss (D) in these regions is associated with microgliosis (E) and astrogliosis (F), shown by a microglial marker [ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1)) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) specific immunohistochemistry, respectively.