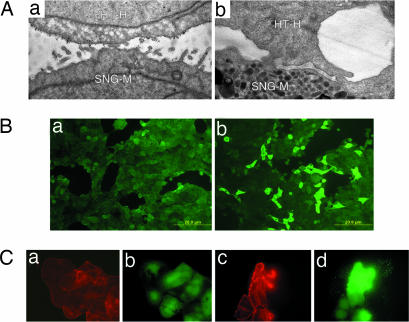
Fig. 1.
Activation of HT-H cells by trophinin-mediated cell adhesion. (A) Electron micrographs of HT-H cells 10 min (a) and 6 h (b) after adhesion to trophinin-expressing endometrial SNG-M cells (10). Gold particles represent anti-trophinin antibodies. (B) An HT-H monolayer was incubated in medium containing Na3VO4, overlaid without (a) or with (b) HT-H cell suspension and stimulated for phosphorylation at 37°C for 30 min. Adhered HT-H cells were removed by gentle pipetting, and the HT-H monolayer was stained with anti-phosphotyrosine (pY) antibody to detect tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. (C) HT-H cells treated for anti-trophinin antibody cross-linking and phosphorylation stimulation. HT-H cells were reacted with the second antibody only (a and b) and with anti-trophinin antibody followed by a second antibody (c and d). The cells were stained with rhodamine–phalloidin for F-actin (red) and an anti-pY antibody (green).