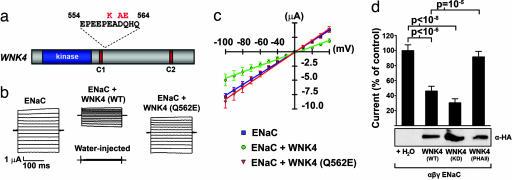
Fig. 1.
Wild-type WNK4, but not PHAII-mutant WNK4, inhibits ENaC by way of a kinase-independent mechanism. cRNA encoding the indicated proteins was injected into Xenopus oocytes, and amiloride-sensitive, whole-cell Na+ currents were recorded as describe in Methods. (a) A diagram showing the clustering of PHAII-causing mutations in WNK4. (b) Representative current tracings from oocytes expressing ENaC alone, ENaC plus wild-type WNK4, or ENaC plus PHAII–WNK4. (c) Current–voltage (I–V) relationships of oocytes expressing indicated constructs from a representative experiment plotted as mean ± SE of the Na+ currents for each experimental group. (d Upper) Cumulative results of amiloride-sensitive currents measured at −100 mV are shown as a proportion of the ENaC control. Each group expresses ENaC plus the indicated construct; a minimum of 29 oocytes were studied in each group. The significance of differences between groups was calculated with two-tailed Student's t test. (d Lower) Results of Western blotting of oocyte lysates shows the expression of WNK4-HA in the corresponding experimental groups.