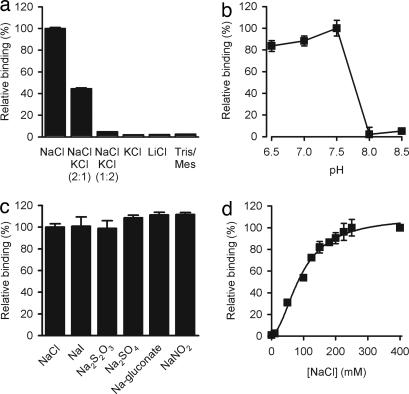
Fig. 3.
Tyrosine binding to Tyt1 is strictly Na+- and pH-dependent. (a) Binding of l-[3H]tyrosine to solubilized Tyt1 was performed in assay buffer composed of 50 mM Tris/Mes, pH 7.5/20% glycerol/2 mM TCEP/0.05% N-dodecyl-β-d-maltopyranoside/150 mM of the indicated salts (at the indicated ratios) (n = 6). (b) The effect of protons on the binding activity was performed by varying the pH of the assay buffer in the presence of 150 mM NaCl (n = 6). (c) Tyrosine binding to solubilized Tyt1 is not chloride-dependent as determined by the replacement of NaCl with other sodium salts. (d) Tyt1 exhibits an apparent 2 Na+:1 tyrosine binding stoichiometry. The apparent Na+-activation constant of l-tyrosine binding (KDNa+) was determined to be 91.5 ± 4 mM with a Hill coefficient of 1.94 ± 0.28. Binding of 1 μM l-[3H]tyrosine was performed by varying the NaCl concentration from 0–400 mM (equimolar replacement with Tris/Mes; n = 3).