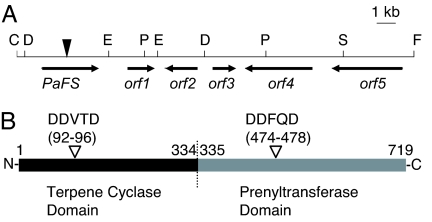
Fig. 2.
Chromosome map around PaFS and the primary structure of PaFS. (A) Chromosome map. A filled reverse triangle indicates the starting point of genome walking. The restriction sites for ScaI, DraI, EcoRV, FspI, PvuII, and StuI used in genome walking are represented by the letters C, D, E, F, P, and S, respectively. The direction and deduced region of transcription are represented by arrows. The deduced orf1, orf2, orf3, orf4, and orf5 represent 2-oxo-glutarate-dependent dioxygenase, P450 monooxygenase, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase, α-mannosidase, and Nop14 like genes, respectively. Homology searches were performed by using BLAST (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/). (B) Schematic of two putative domains of PaFS. Black and gray bars indicate the terpene cyclase domain and the prenyltransferase domain, respectively. Reverse open triangles indicate the DDxxD motives of both domains. The borders between the terpene cyclase domain and the prenyltransferase domain were deduced by the homology with other fungal aristolochene synthases or GGSs.