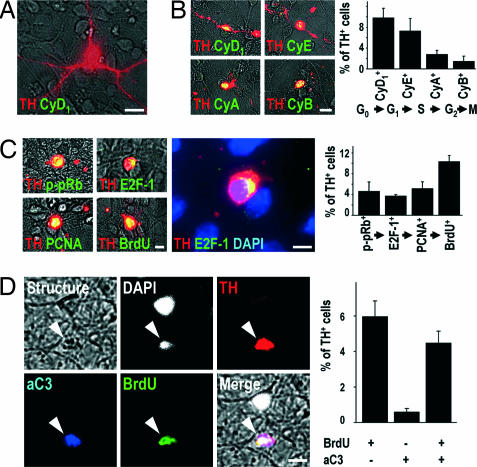
Fig. 4.
Cell-cycle events do not occur in postmitotic TH+ midbrain neurons in vitro under control conditions (A), but are observed after MPP+ intoxication (B–D). (A) In control cultures, cell cycle-associated proteins, such as cyclin D1 (CyD1, green) were never expressed in TH+ neurons (red). (B) However, after 24 h of intoxication with MPP+, the G1-phase-associated CyD1, the S-phase-associated cyclin E (CyE), the G2-phase-associated cyclin A (CyA), and the M-phase-associated cyclin B (CyB) (green) were expressed in TH+ cells (red). The graph shows the percentage of TH+ cells expressing CyD1, CyE, CyA, and CyB after 24 h of MPP+ intoxication. (C) Immunoreactivity for the S-phase-associated markers p-pRb, E2F-1, PCNA, and BrdU (green) was detected in TH+ DNs (red) after 24 h of MPP+ intoxication. Visualization of chromatin with DAPI (blue) demonstrated the perinuclear expression of E2F-1 (green) in TH+ neurons (red). The graph shows the percentage of TH+ cells immunoreactive for p-pRb, E2F-1, PCNA, and BrdU after 24 h of MPP+ intoxication. (D) A 24-h treatment of cultured neurons with MPP+ led to the appearance of morphologically disintegrated cells (structure, gray) with condensed chromatin (DAPI, white) and dopaminergic phenotype (TH+, red) that were immunopositive for both the activated form of the downstream effector caspase-3 (aC3, blue) and BrdU (green). The graph shows the quantification of the presence (+) or absence (−) of BrdU and aC3 immunoreactivity in TH+ cells after 24 h of MPP+ treatment. [Scale bars: 20 μm (A and B); 10 μm (C and D).]