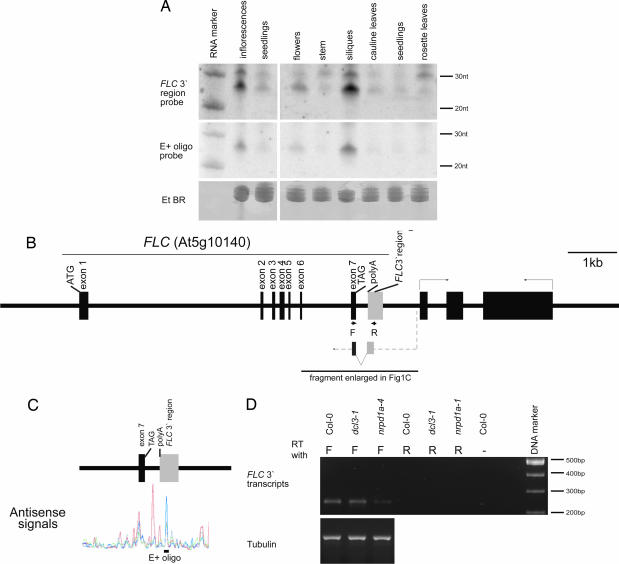
Fig. 1.
Detection of small RNAs and antisense transcripts in FLC 3′ region. (A) Distribution of FLC 3′ small RNA in different organs and developmental stages of Arabidopsis. Total RNA isolated from different tissues of Arabidopsis was hybridized with either a 300-nt FLC 3′ fragment or an oligonucleotide (E+) that had shown strong hybridization in the whole-genome tiling arrays (12). The ethidium bromide staining is shown as a loading control. (Left) Prolonged exposure of a Northern blot carrying RNA isolated from seedlings and inflorescences. (Right) Northern blot hybridization to RNA isolated from different organs and stages of Arabidopsis. An RNA marker resolved on the same gel was used to size the FLC small RNA. (B) Schematic representation of the FLC locus with exons shown as thick black bars and introns represented by black lines joining the exons. The gray rectangle represents the FLC 3′ region described in the paper. A schematic representation of the antisense transcript and location of primers used to amplify it are also shown. (C) Representation of the data from ref. 12 of the antisense signals detected in 3′ region of FLC. Poly(A)+ RNA had been extracted from different tissues: mixed-stage flowers (blue), seedlings (red), root (green), and cell culture (black). The location of the E+ oligonucleotide probe is shown. (D) Detection of an antisense transcript from the 3′ end of FLC by ssRT-PCR in seedlings of Col-0, dcl3-1, and nrpd1a-4.