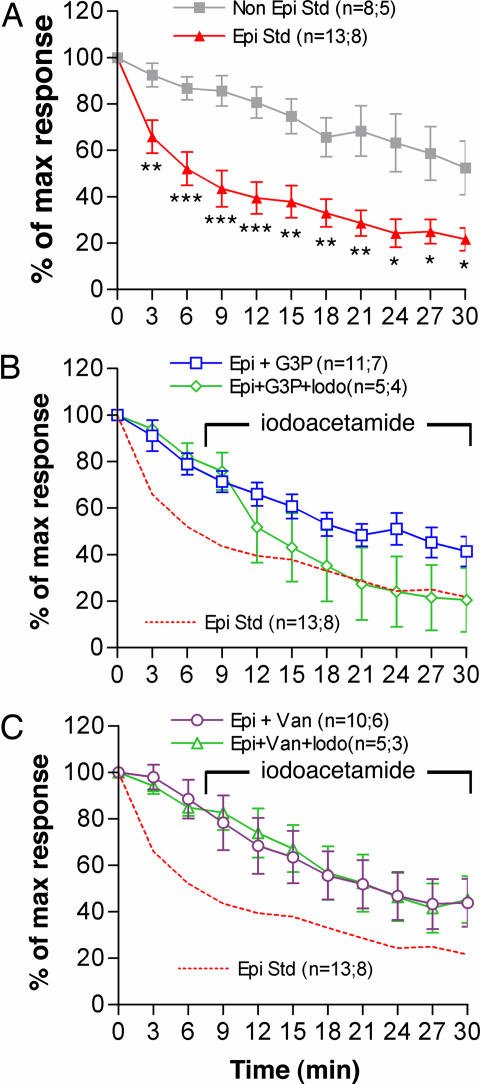
Fig. 4.
Comparison of GABAA current rundown in neurons from epileptogenic and nonepileptogenic cortex and correlation with receptor endogenous phosphorylation. (A) Averaged normalized current in standard condition (Std) for neurons from epileptic (Epi) and nonepileptic (Non Epi) patients. Student's t test at each time comparisons: ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001. (B) The addition of G3P (500 μM) to the pipette milieu markedly reduced rundown in neurons from epileptic patients (Epi+G3P); this effect is counteracted by the addition of iodoacetamide (500 μM) to the bath (Epi+G3P+Iodo). (C) Protective effect against rundown in neurons from epileptic patients of orthovanadate (100 μM) added to the pipette milieu (Epi+Van) and lack of a counteracting effect by iodoacetamide (500 μM) on this protection (Epi+Van+Iodo). Iodoacetamide addition started between GABA application times t = 6 min and t = 9 min and was maintained thereafter (B and C). For each curve, the parentheses indicate, respectively, the number of neurons and the number of corresponding patients. The error bars indicate SEM. Statistical analysis is presented in Table 1.