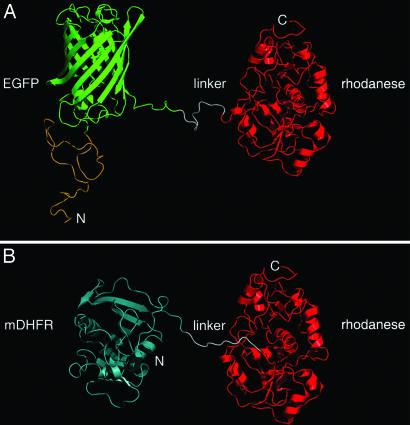
Fig. 1.
Models of the EGFP–rhodanese and mDHFR–rhodanese chimeras. (A) In the EGFP–rhodanese chimera, the C terminus of EGFP (green) is connected to the N terminus of rhodanese (red) by a linker peptide of 11 residues (white). The N terminus of EGFP is fused to a peptide of 39 aa with an N-terminal His6-tag (yellow). (B) In the mDHFR–rhodanese chimera, the C terminus of mDHFR (cyan) is joined to the N terminus of rhodanese (red) via a linker peptide (white) of 15 residues that contains His6-tag. Rhodanese (29), EGFP (19), and mDHFR (30) are represented by ribbon diagrams of their crystal structures (Protein Data Bank codes 1RHD, 1EMA, and 1U70, respectively). In the case of mDHFR, the only available crystal structure corresponds to a mutant ternary complex. The N and C termini of the chimeras are indicated.