Fig. 3.
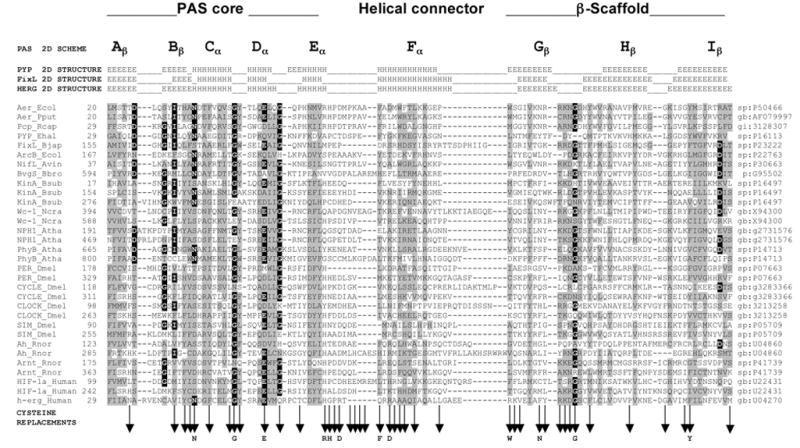
Multiple alignment of selected PAS domains, showing the secondary structures of PYP, FixL and HERG, and sub-domains of the crystallographic structure of PYP (adapted from Taylor and Zhulin, 1999). The variable N-terminal cap is not included in the alignment. Residues in reverse contrast are identical in >50% of the sequences of >300 PAS domains. Shaded residues are similar in >75% of the sequences. Vertical arrows beneath the alignment indicate cysteine replacements. A residue shown below a vertical arrow indicates that the cysteine replacement mutation at this site produced a defective aerotaxis phenotype. A complete alignment of PAS domain sequences is maintained at www.llu.edu/medicine/micro/PAS
