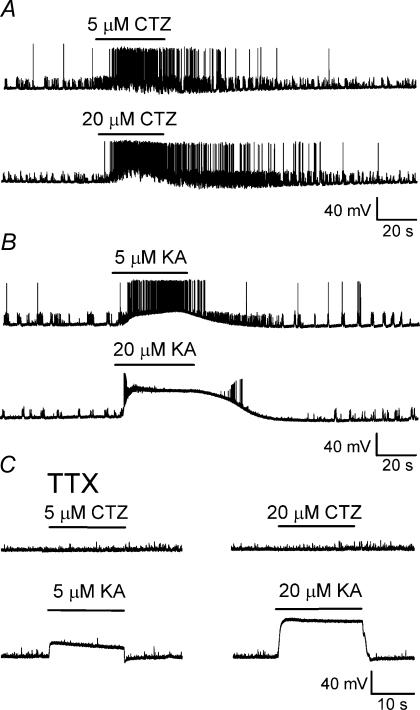
Figure 7. CTZ increases action potential firing but does not directly induce membrane depolarization.
A, bath application of 5 μm (upper trace) and 20 μm CTZ (lower trace) increased the firing frequency of spontaneous action potentials. As expected, 20 μm CTZ has a stronger stimulatory effect on neuronal firing. B, bath application of 5 μm KA (upper trace) also increased the frequency of action potentials, but was accompanied with an obvious membrane depolarization. After application of 20 μm KA (lower trace), a strong membrane depolarization resulted in inactivation of sodium channels and suppression of action potentials. A and B are from the same neuron. C, in the presence of TTX, spontaneous and evoked action potentials were totally blocked. CTZ (5 μm and 20 μm) application did not induce any membrane depolarization (upper traces), whereas KA (5 μm and 20 μm) application still induced significant membrane depolarization (lower traces). All recordings in C are from the same neuron.