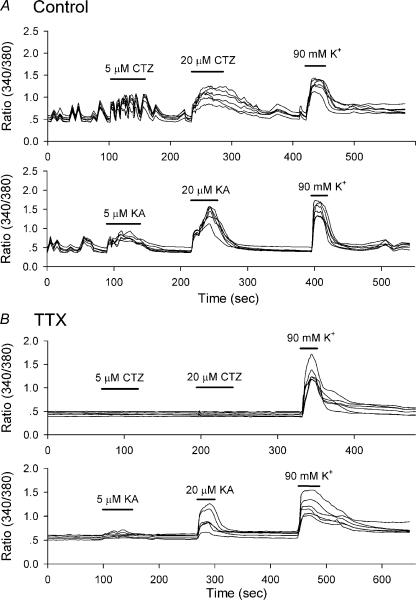
Figure 9. CTZ-induced intracellular calcium increase is activity dependent.
A, bath application of CTZ (upper traces) and KA (lower traces) increased intracellular calcium concentration [Ca2+]i in normal bath solution; 90 mm KCl stimulation serves as positive control for neuronal calcium response. B, in the presence of TTX (0.5 μm), bath application of CTZ (upper traces) did not increase the [Ca2+]i, whereas KA still effectively induced calcium responses.