Figure 3.
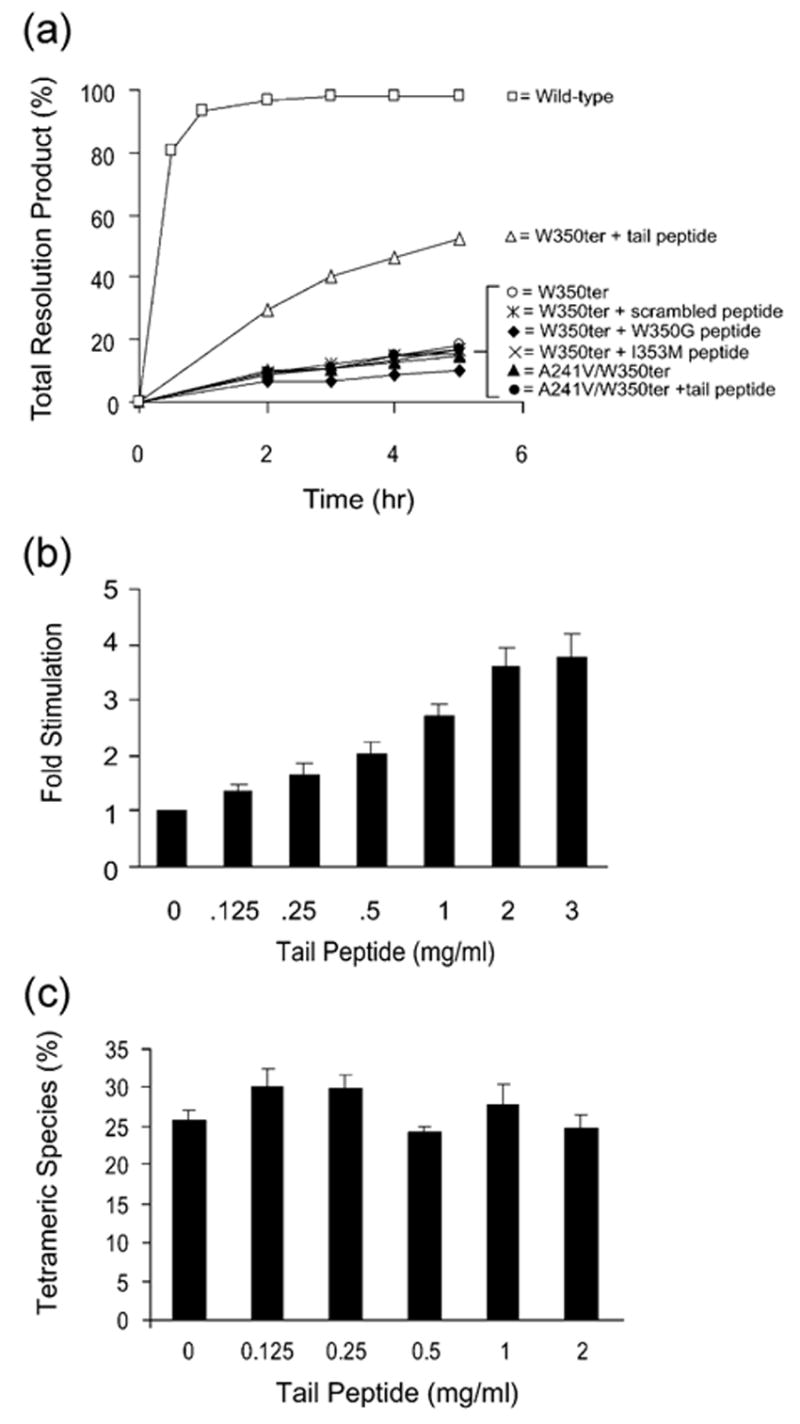
W350ter Holliday junction resolution activity is specifically stimulated by the heptameric C-terminal tail peptide. (a) Holliday junction resolution by the indicated wild-type or mutant Int proteins in the absence or presence of the indicated heptameric peptide (2 mg/ml). (b) Relative fold stimulation of W350ter Holliday junction resolution by tail peptide in varying concentrations in comparison to reactions without tail peptide incubated at 20 °C for four hours. (c) Gel mobility shift assay of 32P-labeled Holliday junction incubated with W350ter at 20 °C for ten minutes in the absence or presence of heptameric C-terminal tail peptide. Reaction conditions were the same as the resolution assays (Figures 2(a) and (b) and 3(a)) except for the presence of EDTA (1 mM) and glycerol (5%). Binding reactions were analyzed by electrophoresis at 25 °C on 7% polyacrylamide Tris–borate–EDTA (pH 8.1) gels. Quantification with a Fuji BAS-2500 phosphorimager was used to determine the percent of tetrameric Int–Holliday junction complex; any small amounts of resolution product (less than 3%) were considered to have been part of the Int–Holliday junction complex. The concentration of W350ter was determined by titration to be well within the linear range for tetramer formation and the amount of tetrameric complex bound at ten minutes is below half-maximal (data not shown). All peptides were custom synthesized and HPLC purified to 95% purity by AnaSpec, Inc. and stored lyophilized at −20 °C. Stock solutions of peptide were dissolved in sterile, de-ionized water to a concentration of 4 mg/ml and stored frozen at either −20 °C or in liquid nitrogen.
