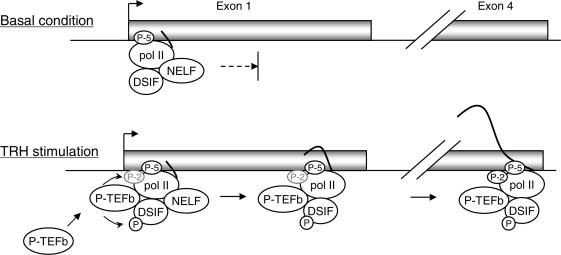
Figure 5.
A model for the mechanisms by which the DSIF–NELF complex and P-TEFb control MKP-1 transcription. In basal condition, the DSIF–NELF complex associates with pol II arrested in the promoter-proximal region. TRH stimulation induces recruitment of P-TEFb to the pol II complex resulting in phosphorylation of the CTR of Spt5 and of the CTD of pol II. This leads to the dissociation of the DSIF–NELF complex and the progression of pol II elongation. P-TEFb and DSIF remain associated with pol II during elongation of the transcript, possibly contributing also to the control of RNA processing and maturation.