Figure 1.
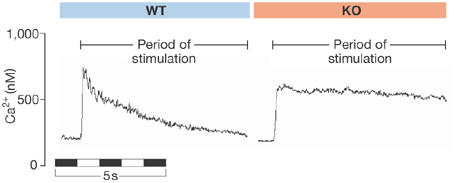
Ca2+ response of isolated myocytes to the application of caffeine. Caffeine was added just before the rapid rises in Ca2+. Caffeine induces the release of Ca2+ stores from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In the myocyte from a wild-type (WT) mouse, Ca2+ rises and then declines as it is removed from the cell by the Na/Ca exchanger (NCX). In a myocyte in which the NCX has been knocked out (KO) , Ca2+ rises and remains elevated.
