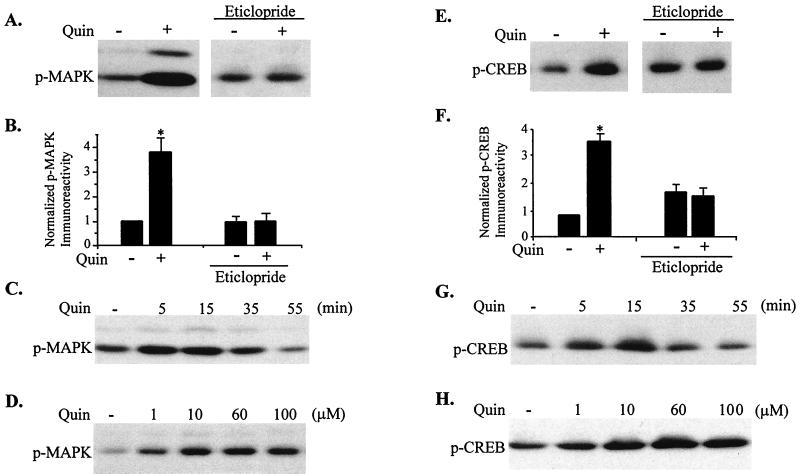
Figure 1.
Stimulation of phosphorylation of MAPK and CREB by the D2 dopamine receptor agonist quinpirole. (A and E) Immunoblots of phospho-MAPK (A) and phospho-CREB (E). Brain slices were preincubated in the absence or presence of the D2 antagonist eticlopride (40 μM) for 20 min, followed by incubation with or without the D2 agonist quinpirole (60 μM) for 15 min. Extracts of slices were immunoblotted with anti-phospho-MAPK or anti-phospho-CREB antibody. (B and F) Quantitation of p42 MAPK phosphorylation (B) and CREB phosphorylation (F). ∗, P < 0.01, compared with minus quinpirole. (C and G) Time courses of the D2 receptor-induced phosphorylation of MAPK (C) and CREB (G). Slices were treated with quinpirole (60 μM) for the indicated times, and phospho-MAPK and phospho-CREB were detected by immunoblotting of slice extracts. (D and H) Dose-dependence of the D2 receptor-induced phosphorylation of MAPK (D) and CREB (H). Slices were treated with quinpirole for 15 min at the indicated concentrations, and phospho-MAPK and phospho-CREB were detected by immunoblotting of slice extracts.