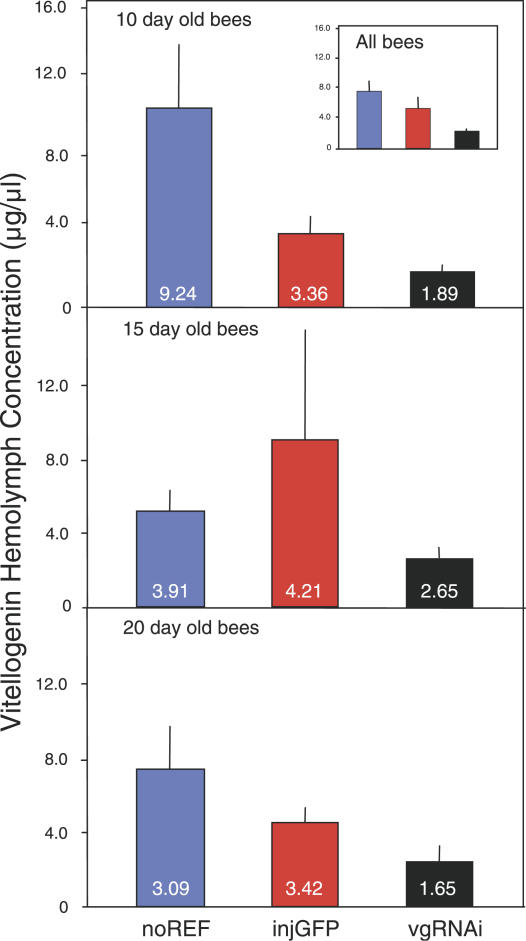
Figure 1. The Effect of vitellogenin RNAi on Hemolymph Vitellogenin Concentrations.
Levels are in micrograms per microliter relative to a β-galactosidase standard. Significant suppression of vitellogenin is apparent in RNAi knockdowns (vgRNAi) compared to injected controls (injGFP; Mann-Whitney U test: Z = 2.84, n = 54, p < 0.005). Control injections (GFP-derived dsRNA) did not significantly affect the vitellogenin level of the bees compared to the non-injected reference group (noREF; Mann-Whitney U test: Z = −1.10, n = 55, p = 0.27). Bars show results as means and standard errors with corresponding medians at the bottom of each bar. Because the dataset did not conform to assumptions of parametric tests (see Materials and Methods), medians can be considered the more accurate statistic. The dataset is split by age (10, 15 and 20 d olds) to visualize the persistence of RNAi. However, age did not affect the vitellogenin level of the workers (p = 0.68, see data analysis section for details), and thus conclusions cannot be drawn about treatment effects by age. The means and standard errors of the dataset overall are shown in the embedded box of the upper panel (medians for the dataset: noREF = 3.94, injGFP = 3.45, and vgRNAi = 2.46).