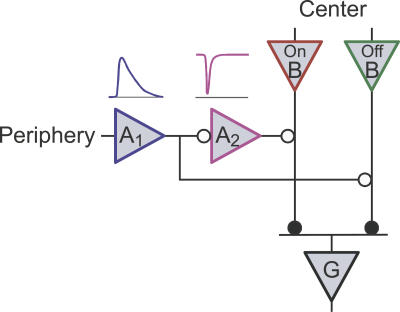
Figure 7. An Amacrine Cell Circuit to Explain Polarity Reversal.
An On-Off ganglion cell (G) receives excitatory input (closed circles) from On and Off bipolars (B) in the receptive field center, whose gain is modulated by presynaptic inhibition from amacrine cells (open circles). The peripheral shift depolarizes (see time course above A1) an amacrine cell (A1), which in turn suppresses transmission from the Off bipolar channel. Amacrine A1 also inhibits a second amacrine (A2), which leads to transient disinhibition (see time course above A2) of the On bipolar pathway. See text for details.