Fig. 2.
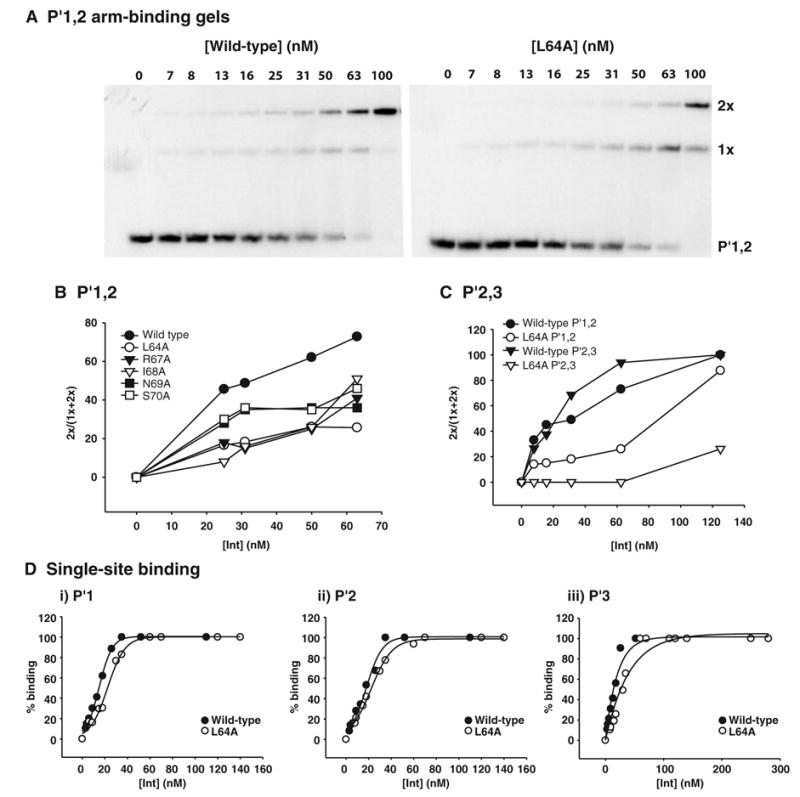
Residues within the 64–70 region are required for cooperative arm-binding. Full-length Int, various mutant proteins were tested in gel shift assays for their abilities to bind to the following arm-type DNA substrates; (A,B) 50 bp P′1,2, (C) 50 bp P′2,3 double arm-type sites and (D) 40 bp P′1, P′2 and P′3 single arm-type sites. The indicated concentrations of proteins were mixed with 50 nM and 10 nM radiolabelled DNA substrate for the single and double arm-type substrates, respectively, and incubated at 19°C for 30min. Reactions were analysed by electrophoresis on native 8% polyacrylamide gels which were subsequently dried and visualized by autoradiography. The intensity of the bands was measured as described in Experimental procedures. For the double and single arm-type sites the ratio of the doubly bound species to the total amount of substrate bound and the total amount of substrate bound has been calculated, respectively, and plotted as a function of protein concentration. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments.
