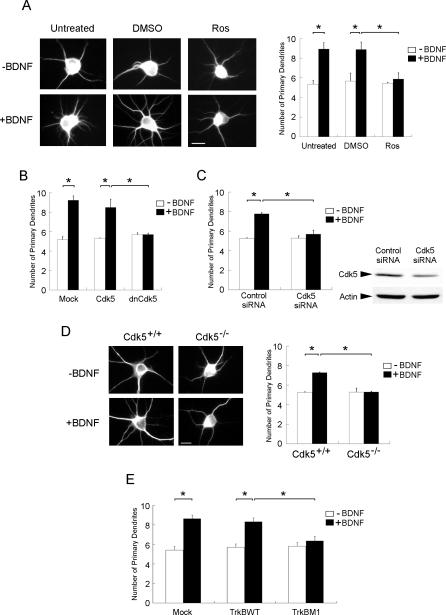
Figure 5. Attenuation of Cdk5 Activity Abolished BDNF-Induced Increase in Primary Dendrites in Hippocampal Neurons.
(A) Hippocampal neurons were stimulated with BDNF for 3 d in the presence or absence of Ros (10 μM). Interestingly, while BDNF treatment markedly enhanced the number of primary dendrites, treatment with Ros abrogated the increase.
(B) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with Cdk5 or DN Cdk5. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were exposed to BDNF for 3 d. Overexpression of DN Cdk5 abolished the BDNF-induced increase in primary dendrites.
(C) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with Cdk5 siRNA or control siRNA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were exposed to BDNF for 3 d. Transfection with Cdk5 siRNA attenuated Cdk5 expression in hippocampal neurons. More importantly, BDNF-induced increase in primary dendrites was abrogated in Cdk5 siRNA–transfected cells.
(D) Hippocampal neurons isolated from cdk5 +/+ and cdk5 −/− brains were treated with BDNF for 3 d. BDNF treatment failed to enhance primary dendrites in Cdk5−/− neurons.
(E) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with TrkB WT or TrkB M1. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were exposed to BDNF for 3 d. Overexpression of TrkB M1 markedly reduced the BDNF-induced increase in primary dendrites.
Scale bar = 10 μm. *, p < 0.05.