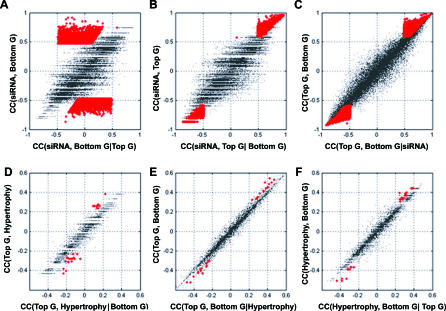
Figure 3. Identification of the Top and Bottom Gene Pairs and the Causal Genes for PPARα–AILH by the Two-Step Relay Approach.
Conditional independency between the instrumental variable (Ppara) and the bottom gene given the top gene in selected gene pairs (A–C) is illustrated. When conditioned on the identified top genes, indicated in red (A), the correlation between siRNA effect, manifested by Ppara mRNA level and the bottom genes, vanishes. However, when conditioned on the bottom genes, indicated in red (B), the correlation between Ppara and the selected top genes remains significant. Similarly, the dependency between the top genes and liver hypertrophy is abolished when conditioned on the bottom genes (p < 0.01), indicated by red dots in (D). The dependency between the top genes and bottom genes remains when conditioned on liver hypertrophy (E), as does the dependency between liver hypertrophy and the bottom genes (p < 0.01) when conditioned on the top genes, indicated by red dots (F). To assess the false-positive rate among the derived relationships after multiple tests, Monte Carlo simulation was done. The estimated false-positive rate for the 15 genes and one EST inferred to mediate PPARα–AILH after testing all of the top and bottom gene pairs is 0.002.