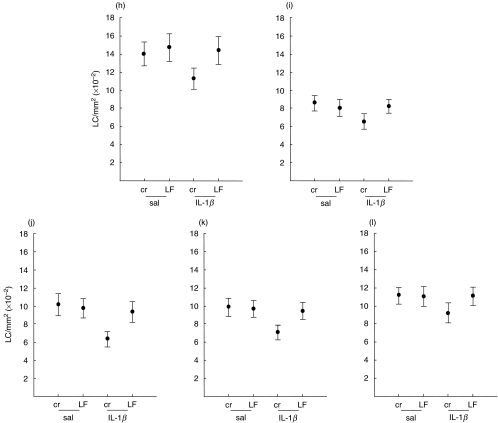
Fig. 3.
Inhibition by LF of IL-1β-induced changes in epidermal CD1a+ LC frequency. Volunteers (h–l) were exposed topically at two sites to LF (50 µl) and at a further two sites to an equivalent volume of aqueous cream alone. Two hours later, IL-1β was injected intradermally into paired sites (one pretreated with LF and one with cream) and biopsies taken 2 h later. CD1a+ LC densities were assessed following indirect immunofluorescence staining of epidermal sheets. Results are expressed as the mean ± s.d. number of cells/mm2 derived from examination of 50 fields/sample. The percentage reduction in frequency of CD1a+ LC induced by IL-1β (at sites pretreated with cream) was: (h) 19·0%; (i) 17·6%; (j) 23·9%; (k) 37·6%; (l) 28·2%. In all cases, prior treatment with LF inhibited the IL-1β-induced response.