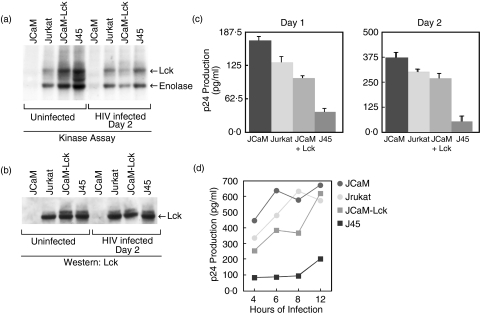
Fig. 1.
Lck kinase activity inversely correlates with HIV replication. Jurkat T cells or Jurkat-derived JCaM, J45, or JCaM transfected with wild-type lck cDNA (JCaM-LCK) were infected with HIV-1IIIB (moi 1·5) and cell cultures assayed for p24 antigen. (a) The level of kinase activity of the various Jurkat-derived cell lines using an in vitro kinase assay of uninfected cells and HIV infected cells after 2 days. Equal amounts of cell equivalents were immunoprecipitated from cellular lysates using anti-Lck. The immunocomplexes were incubated with [γ32P]ATP, the proteins fractionated by SDS-PAGE, electrotransferred to Immobilon-P membranes, and the radiolabelled proteins were visualized by autoradiography. Results show both autophosphorylation of Lck and phosphorylation of an exogenous substrate, rabbit muscle enolase. These results are representative of three independent experiments. (b) The Lck protein level of the various Jurkat-derived cell lines, uninfected and after HIV infection for 2 days, determined from total cellular lysates from (a), using Western immunoblotting with anti-Lck and ECL. Equal loading of total protein was based on equal cell equivalents for each lysate. These results are representative of three independent experiments. (c) The relative level of viral p24 antigen determined by ELISA for each Jurkat-derived cell line infected with HIV-1IIIB after 1 or 2 days of infection. Cells (106/ml) were infected with HIV-1IIIB (moi 1·5) for 2 h, washed, and cultured for the indicated days prior to gag p24 measurement. Results represent the mean p24 antigen level ± SEM of triplicate cultures. These results are representative of at least five independent experiments. (d) p24 antigen production from the various Jurkat-derived cell lines after varying the length of time of initial HIV-1IIIB infection, from 4 to 12 h. Results represent the average p24 antigen level of duplicate cultures. The results shown are for 2 days after initial HIV-1 infection.