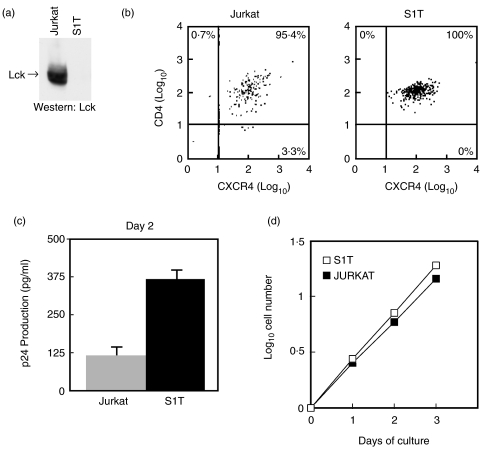
Fig. 3.
Lack of Lck kinase facilitates HIV productive infection. (a) The S1T human T cell line lacks Lck protein compared with Jurkat T cells. 2 × 107 Jurkat and S1T T cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated with anti-Lck, the proteins separated by SDS-PAGE and electrotransferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membrane was blocked with 5% skim-milk and Lck protein identified by Western immunoblot with anti-Lck using ECL readout. (b) Two-colour FACS analysis of cell surface CD4 and CXCR4 using Jurkat and S1T human T cell lines. (c) Relative viral p24 antigen production from Jurkat and S1T cells determined after 2 days following infection with HIV-1IIIB (moi, 1·5). The amount of entry virus was determined to be 157 and 151 pg of p24gag, respectively (Table 1). Results represent the mean p24 antigen level ± SEM of triplicate cultures. These results are representative of two independent experiments. (d) Exponential increase in cell number by Jurkat and S1T T cell lines over time in culture. Cells were seeded at 2 × 105 cells/ml and aliquots withdrawn and cells counted over the indicated days of culture. Population doubling times were calculated from the log-phase growing cultures.