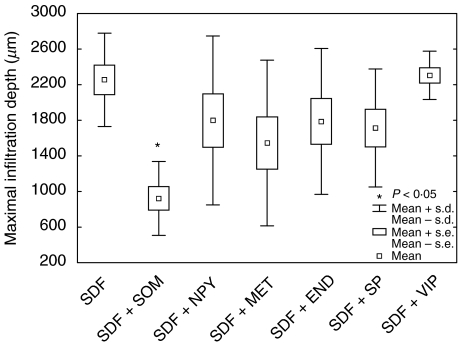
Fig. 2.
Somatostatin (SOM) inhibits chemokine (SDF-1α)-induced infiltration of T cells. Blood T lymphocytes were allowed to migrate into a collagen type I gel (>90% of the infiltrating cells were CD3+). SDF-1α (50 ng/ml) in the gel increased the infiltration depth of T lymphocytes (Fig. 1). This increase was inhibited significantly in the presence of somatostatin (10−8m) in the gel, while neuropeptide Y (NPY, 10−8m), metenkephalin (MET, 10−8m), β-endorphin (END, 10−8m), substance P (SP, 10−8m) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP, 10−8m) in the gel had no effect on SDF-1α-induced infiltration. The figure shows mean maximal infiltration depth determined from three independent experiments and of 10 microscopic fields in each experiment (×100).