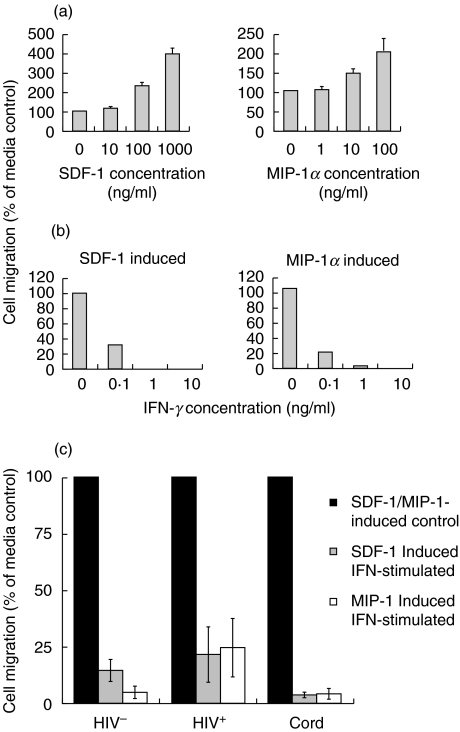
Fig. 4.
IFN-γ down-regulates SDF-1- and MIP-1α-mediated chemotaxis of CD14+ monocytic cells. (a) PBMCs (1 × 105/ml) from HIV-negative adult blood were subjected to chemotaxis using increasing doses of SDF-1 or MIP-1α in order to determine the optimal dose for use in subsequent experiments. Migrated CD14+ monocytes were enumerated by flow cytometry and are expressed as a percentage of the control (cells incubated in the absence of chemokines). The results shown are a mean ± s.d. of three experiments. (b) PBMCs (1 × 105/ml) from HIV-negative adult blood were analysed for chemotaxis towards SDF-1 or MIP-1α after culture with increasing doses of IFN-γ. Migrated CD14+ monocytes were enumerated by flow cytometry and are expressed as a percentage of the unstimulated control. The results shown are a mean of two experiments. (c) PBMCs (1 × 105/ml) from six HIV-negative adults, six cord blood donors and six HIV-infected individuals were cultured for 24 h in the presence and absence of 1 ng/ml of IFN-γ followed by analysis for chemotaxis towards SDF-1 or MIP-1α. Migrated CD14+ monocytes were enumerated by flow cytometry and expressed as a percentage of the unstimulated control.