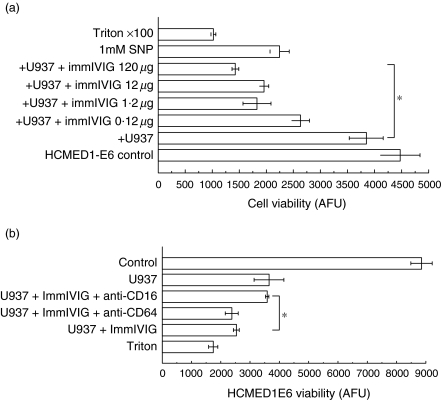
Fig. 6.
Immobilized human polyclonal IgG stimulates macrophages to kill human VSMCs dependent on CD16. VSMCs were loaded with calcein (intracellular fluorescent dye) prior to addition to macrophages and VSMC viability was measured as the retained calcein in arbitrary fluorescence units (AFU) after 4 h co-incubation. (a) x-Axis, HCMED1-E6 viability measured as retained calcein fluorescence (arbitrary fluorescence units, AFU); y-axis, macrophages (U937) and increasing amounts of immobilized human polyclonal IgG were added as indicated. *P < 0·05, χ2 for trend. Triton X-100 (0·1% final) or sodium nitroprusside (1 mm) were added as positive controls. (b) x-Axis, HCMED1-E6 viability measured as retained calcein fluorescence (arbitrary fluorescence units); y-axis, macrophages (U937), immobilized human polyclonal IgG and antagonistic anti-CD16 or anti-CD64 or control soluble mouse IgG1 were added as indicated. Triton X-100 (0·1% final) was a positive control. *P < 0·05 antagonistic anti-CD16 antibodies increased VSMC viability compared to control (Dunn's test).