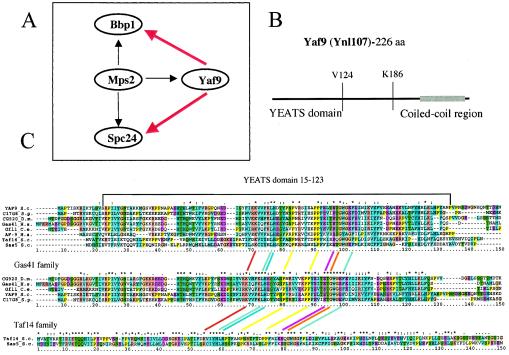
FIG. 1.
Yaf9(Ynl107) interacts with Mps2 in a two-hybrid screen, contains a YEATS domain, and shows most similarity to the family of Gas41-like sequences in metazoans. (A) Yaf9, Spc24, and Bbp1 interact with Mps2 in a two-hybrid screen. The black arrows indicate two-hybrid interactions, and the red arrows indicate synthetic lethality between yaf9Δ and either bbp1-1 or spc24-11 mutants (see Fig. 3A). (B) Schematic representation of the Yaf9 sequence showing the location of the N-terminal YEATS domain and the minimal C-terminal 40-amino-acid sequence interacting with Mps2 in the two-hybrid screen. This C-terminal region contains a predicted 30-amino-acid coiled-coil sequence (gray bar) as detected by the COILS program (41) (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html). V124 and K186 indicate valine-124 and lysine-186 of the Yaf9 sequence. (C) CLUSTALW alignments (26) of YEATS domains found in proteins similar to Yaf9. Shown are YEATS domains from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.c.) Yaf9 (Ynl107), Sas5, and Taf14, Schizosaccharomyces pombe (S.p.) SPAC17G8.07, Drosophila melanogaster (D.m.) CG9207, Caenorhabditis elegans (C.e.) Gfl-1, and Homo sapiens (H.s.) Gas41 and AF9. This analysis shows that Yaf9 and the Gas41 family of proteins contain YEATS domains that are more similar to each other than the YEATS domains found in the human AF9 and the yeast Taf14 and Sas5 proteins. The amino acid color code is as follows: yellow for proline, beige for glycine, purple for acidic residues, orange for basic residues, green for polar residues, light blue for hydrophobic residues, and dark blue for aromatic residues. An asterisk above the column of aligned amino acids indicates 100% identity, two dots indicate highly conserved amino acids, and a single dot indicates similar amino acids.