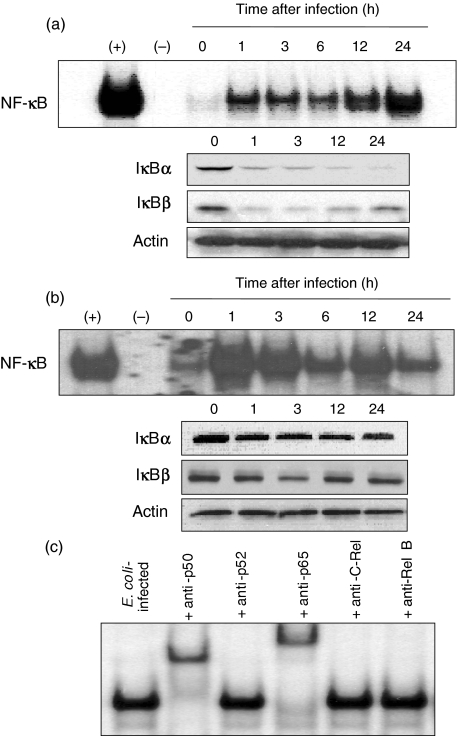
Fig. 1.
NF-κB activation and IκB degradation in human astrocytes infected with E. coli. (a) Primary human astrocytes or (b) U87-MG cell lines were infected with E. coli. NF-κB DNA binding activity at the indicated times was assessed by EMSA. Concurrent immunoblots for IκBα, IκBβ and actin levels in human astrocytes under the same condition are provided beneath each EMSA time point. The results are representative of five repeated experiments. (+) represents positive control in which astrocytes were treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 1 h (–) represents negative control. (c) Activation of specific NF-κB subunits in primary human astrocytes infected with E. coli. Supershift assays were performed using antibodies to p50, p52, p65, c-Rel and Rel B. Antibodies to p50 and p65 shift the entire NF-κB signals. Anti-p50, c-Rel and Rel B did not show the shifts. The results are representative of three repeated experiments.