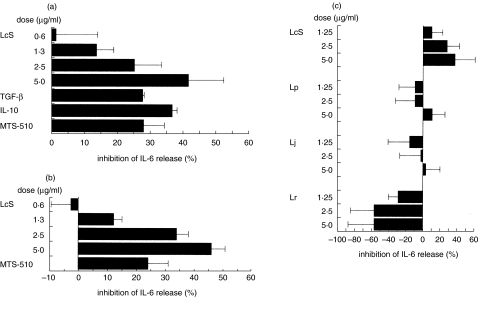
Fig. 1.
Inhibitory effects of heat-killed LcS on IL-6 synthesis in LPS-stimulated murine colonic lamina propria lymphocytes (a) LI-LPMC and (b) RAW264·7 cells. (c) Comparative study of the inhibitory effect among 4 strains of Lactobacillus on the production of IL-6 in LPS-stimulated LI-LPMC. (a, b) These cells were cultured in the presence or absence of both LPS (1 µg/ml) and various doses of LcS and the amounts of IL-6 in the culture supernatants were determined. (c) The inhibitory effects on IL-6 production among four strains of Lactobacillus (L. casei strain Shirota: LcS, L. rahmnosus: Lr, L. johnsonii: Lj, L. plantrum: Lp) were also determined in LPS-stimulated murine LI-LPMC isolated from colitis-afflicted mice. Data represent the percent inhibition of IL-6 synthesis in the cultures stimulated with LPS plus various doses of LcS compared with those stimulated with LPS only. Similar results were obtained from five independent experiments. Data are mean ± SD.