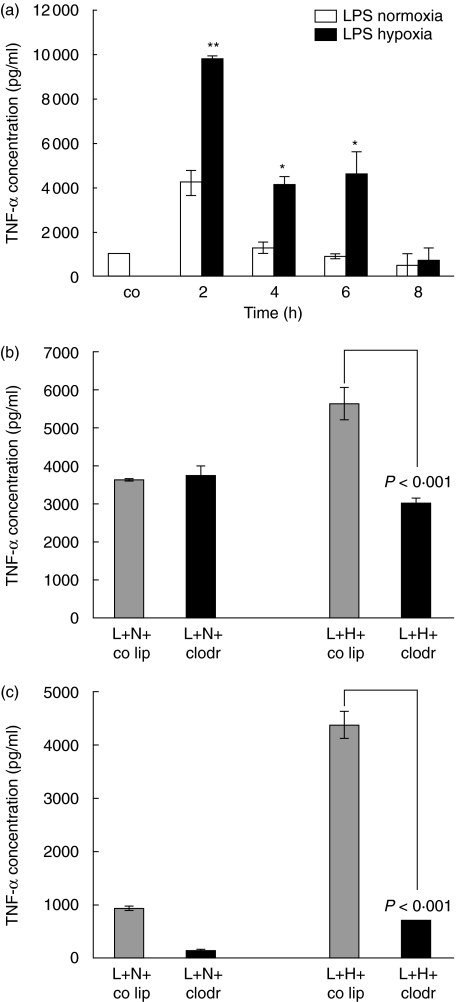
Fig. 4.
(a) Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) protein concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-normoxia and LPS-hypoxia animals. LPS, 150 µg, was instilled intratracheally and animals were exposed to normoxia or hypoxia for 2, 4, 6 and 8 h. Lungs were lavaged, and TNF-α was determined using a standard enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Values are mean ± s.e.m. from five animals. *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 between LPS-normoxia and LPS-hypoxia animals. (b) TNF-α protein concentration in BAL fluid of alveolar macrophage-competent and -depleted animals, exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-normoxia and LPS-hypoxia. Animals were pretreated with control liposomes (co lip) or clodronate-liposomes (clodr); 72 h later 150 µg LPS (L) was instilled intratracheally and animals were exposed to either normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H) for 2 h. TNF-α was determined using a standard ELISA. Values are mean ± s.e.m. from five animals. (c) TNF-α protein concentration in BAL fluid of alveolar macrophage-competent and -depleted animals, exposed to LPS-normoxia and LPS-hypoxia. Animals were pretreated with control liposomes (co lip) or clodronate-liposomes (clodr); 72 h later 150 µg LPS (L) was instilled intratracheally and animals were exposed to either normoxia (N) or hypoxia (H) for 6 h. TNF-α was determined using a standard ELISA. Values are mean ± s.e.m. from five animals.