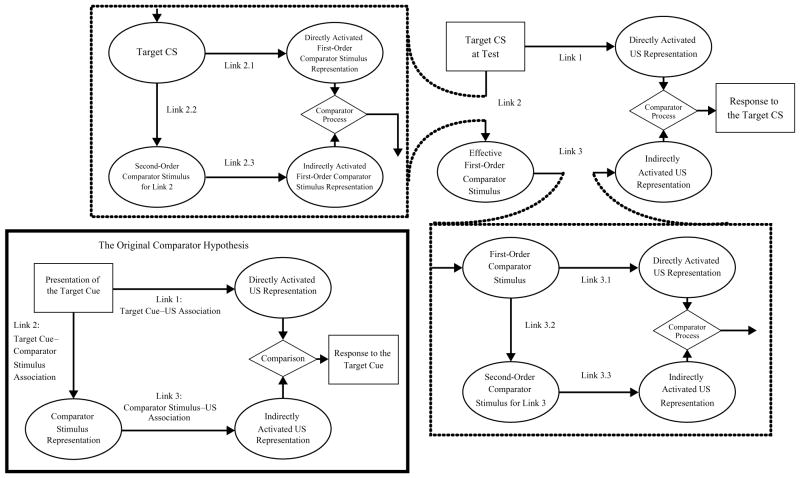
Figure 1.
The lower left panel depicts the original comparator hypothesis (Miller & Matzel, 1988). The remainder of the figure depicts the extended comparator hypothesis (Denniston, Savastano, & Miller, 2001). Applied to extended training of the A–US association following compound training in the present research, the target conditioned stimulus (CS) is X; A is the effective first-order comparator stimulus, and the context is the effective second-order comparator stimulus for Link 3.