FIG. 3.
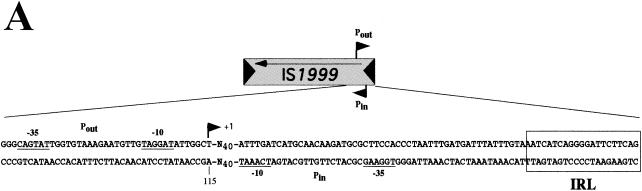
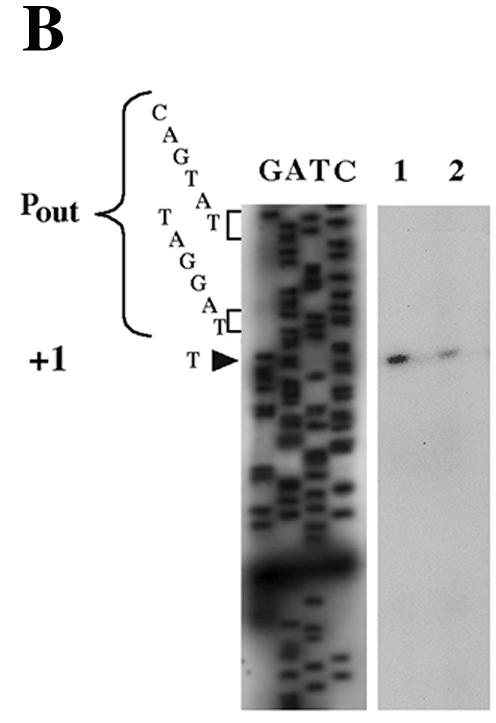
(A) Structure of IS1999. The IS1999 IR are shown by filled triangles. The arrows indicate the orientation of transcription. The outward-directed promoter, Pout, and the promoter of the transposase gene, Pin, are indicated by broken arrows. The −10 and −35 regions for Pin and Pout are underlined. Nucleotide position 115 (according to the sequence GenBank AF133697) in IS1999 corresponds to the transcription start of Pout. The IRL sequence is boxed. (B) Mapping of transcription initiation. Primer Vebprom was extended using RNAs from cultures of E. coli DH10B(pInt-1999-Veb) (lane 1) or P. aeruginosa KG2505(pInt-1999-Veb) (lane 2) as the templates. Equal volumes (2 μl) of the extension product obtained from P. aeruginosa and E. coli were loaded onto the gel. Size markers were from sequencing reactions generated from pInt-1999-Veb DNA primed with Vebprom. G-, A-, T-, and C-specific lanes are indicated. The nucleotide sequences on the left side correspond to that of the complementary strand, which was deduced from the sequencing reaction. The −10 and −35 promoter sequences of Pout regions are shown, and the +1 transcriptional initiation site is indicated by an arrowhead. Similar results were obtained for RNA extracted from E. coli DH10B and P. aeruginosa KG2505 harboring pInt-1999-2000-Veb recombinant plasmid (data not shown).