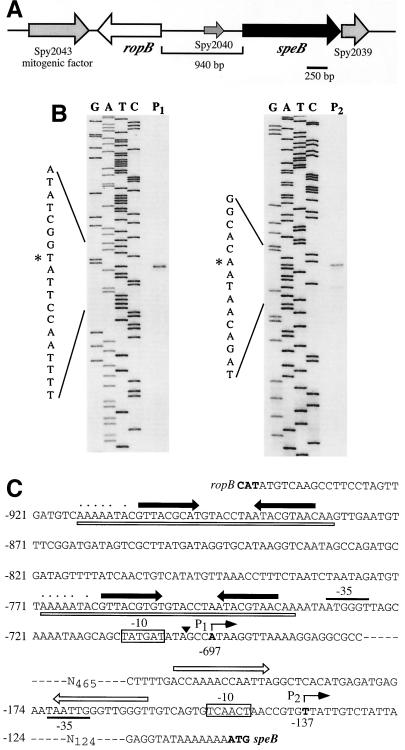
FIG. 1.
Identification of the 5′ ends of the speB transcripts. (A) Organization of the ropB-speB region on the streptococcal chromosome. Gene designations are based on the genome sequence of S. pyogenes SF370 (18). (B) Primer extension analyses to identify the 5′ ends of the two transcripts previously determined for speB. The primer extension products obtained for the longer (P1) and shorter (P2) transcripts are shown. The sequencing ladder used to determine the terminal nucleotides of each transcript (denoted by an asterisk) are shown at the left of the extension products. (C) Features of the P1 and P2 promoters. The initiation nucleotides of the P1 and P2 promoters are in bold and marked by the bent arrow above the sequence. The numbers below the nucleotides and at the left of the sequence indicate nucleotide positions relative to the first nucleotide of the speB start codon. The closed arrows above the sequence show the locations of an inverted repeat present in two copies near P1, and the open boxes beneath the sequence indicate a large direct repeat. Nucleotides that encode a poly(U) tract adjacent to the inverted repeats on the strand opposite to the one shown are indicated by the dotted line above the sequence. The poly(U) tract and repeats have the characteristics of a rho-independent terminator for transcripts encoded on the opposite strand.