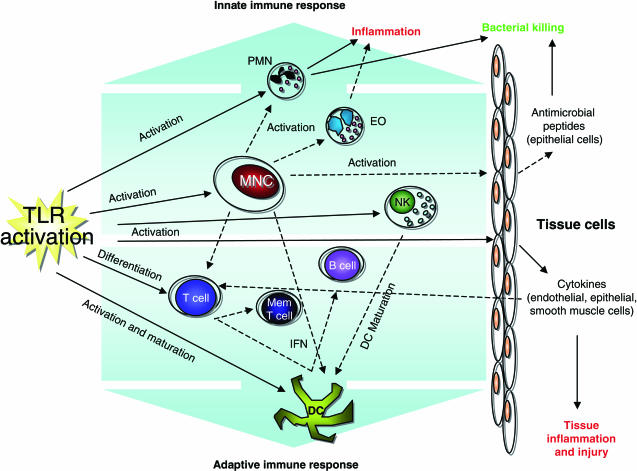
Fig. 1.
Immune pathways activated by Toll-like receptor (TLR) signalling. TLR signalling activates a number of apical pathways that result in the stimulation of both the innate and adaptive immune responses. Mononuclear cells (MNC) in particular serve to amplify TLR activation by the production of cytokines and growth factors. These mediators facilitate communication between different cell types, co-ordinating the recruitment and activation of the immune response network as a whole. Solid arrows illustrate effects of direct TLR activation, dashed arrows represent paracrine actions resulting from TLR activation of an intermediary cell. MNC; mononuclear cells, PMN; polymorphonuclear cells, EO; eosinophils, NK; natural killer cells, DC; dendritic cells, Mem T cell; memory T cell, IFN; interferon.