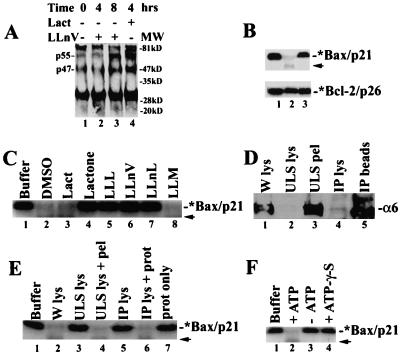
Figure 3.
Bax degradation depends on ubiquitination, proteasome, and ATP. (A) Jurkat cells (0 h) were treated with either 50 μM LLnV or 10 μM lactacystin, followed by preparation of Bax immunoprecipates (with clone 6A7), which were immunoblotted with an ubiquitin antibody. Positions of putative ubiquitinated Bax proteins (p47 and p55) are indicated at left. The nature of the ≈30-kDa and ≈84-kDa bands remains unclear. (B) The 35S-labeled Bax (Upper) or Bcl-2 (Lower) protein (1 μl) were incubated at 37°C for 2 h with either buffer Z only (lane 1) or 100 μg protein extract of MCF-7 cells grown exponentially (lane 2) or pretreated for 8 h with 50 μM LLnV (lane 3). (C) The 35S-labeled Bax protein (1 μl) was incubated with either buffer Z only (lane 1) or 100 μg MCF-7 cell lysate at 37°C for 4 h, in the presence of inhibitors N-carbobenzoxy-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-leucinal (LLL), LLnV, N-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-norleucinal (LLnL), and LLM (100 μM; lanes 3–8) or an equal volume of DMSO (lane 2) in buffer Z. A weak band of ≈16 kDa (indicated by an arrow) is probably an intermediate product of proteasome-mediated Bax degradation. (D) The proteasome in MCF-7 whole-cell lysate (W lys, lane 1) was precipitated by using either ultraspin (ULS) or a proteasome subunit α6 antibody (IP). Both supernatant (lanes 2 and 4) and pellet (lanes 3 and 5) fractions were examined by Western blot assay using antibody to the proteasome α6 subunit (33 kDa). (E) Bax degradation assay was performed as in B, with addition of buffer Z (lane 1) or 100 μg protein from MCF-7 whole-cell lysate (lane 2), ultraspun supernatant (lane 3) or plus the pellet (lane 4), immunodepleted supernatant (lane 5), or plus a purified 20S proteasome (2 μg; lane 6), or the purified proteasome alone (2 μg; lane 7). (F) Bax degradation assay was performed as in B, in the absence (lane 3) or presence of 10 mM ATP (lane 2) or 10 mM ATP-γ-S (lane 4).