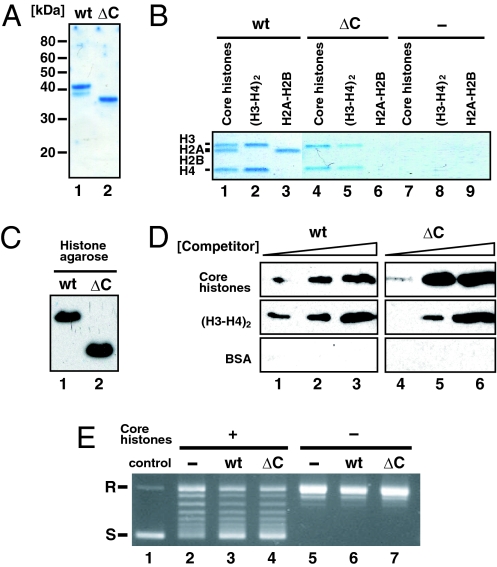
Fig. 1.
Functional activities of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHATΔC. (A) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of purified SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT WT (lane 1) and ΔC (lane 2) proteins. (B) Complex formation of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT with core histones. After incubating histones H2A–H2B, H3, and H4, or all four core histones with Ni-NTA agarose beads, which captured SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT WT (lanes 1–3), ΔC (lanes 4–6), and no protein (lanes 7–9), the bead-bound fraction was resolved by SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (C) Interaction of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT WT (lane 1) and ΔC (lane 2) proteins with histone–agarose. (D) Histone binding specificity of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT WT and ΔC by competition assay. Shown is eluted SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT in supernatant after addition of 100 pmol (lanes 1 and 4), 350 pmol (lanes 2 and 5), and 1,000 pmol (lanes 3 and 6) of competitor proteins [core histones, (H3-H4)2, and BSA] to SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT-bound histone–agarose. (E) Histone chaperone activity of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHATΔC. Circular plasmid DNA (lane 1) was relaxed by topoisomerase I and then incubated with (lanes 2–4) or without (lanes 5–7) core histones plus SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT WT (lanes 3 and 6), SET/TAF-Iβ/INHATΔC (lanes 4 and 7), or no protein (lanes 2 and 5). Under these conditions, a small amount of supercoiled DNA formed in the absence of SET/TAF-Iβ/INHAT (lane 2). R, relaxed; S, supercoiled.