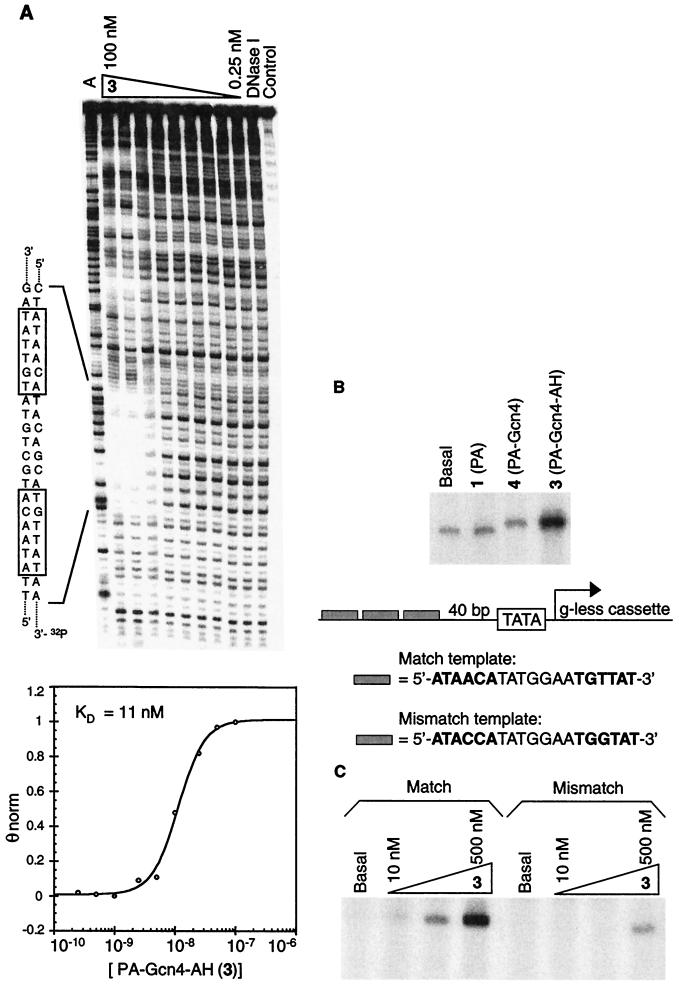
Figure 2.
Conjugate 3 (PA-Gcn4-AH) binds to its cognate palindromic DNA site and activates transcription in vitro when its predetermined DNA binding sites are present. (A) (Upper) Storage phosphor autoradiogram of a quantitative DNase I footprinting titration of 3 on the 3′-32P-labeled 271-bp pPT7 EcoRI/PvuII restriction fragment carried out according to established protocols (15, 21). Preequilibration of 3 with the DNA fragment was carried out for 75 min before initiation of the cleavage reactions. From left to right the lanes are: the A sequencing lane; DNase I digestion products in the presence of 3 at concentrations of 100 nM, 50 nM, 25 nM, 10 nM, 5 nM, 2.5 nM, 1 nM, 0.5 nM, and 0.25 nM, respectively; DNase I digestion products with no 3 present; undigested DNA. (Lower) Data for 3 in complex with the 19-bp palindromic site. The curve through the data points is the best-fit cooperative Langmuir binding titration isotherm (n = 2) obtained from a nonlinear least-squares algorithm. (B) An in vitro transcription reaction containing PA-Gcn4-AH (3) at 200 nM shows enhanced expression of a 277-nt transcript relative to basal levels whereas a reaction containing conjugate 4, lacking the activating region, does not. Inclusion of the parent hairpin polyamide (1) (lane 2) in the reaction does not impair basal transcription (lane 1). The variation in transcript position for lane 4 is caused by curvature of the gel and was confirmed by additional experiments (data not shown). (C) In vitro transcription reactions containing 3 (PA-Gcn4-AH) with templates bearing either the cognate palindromic binding sites (match template) or palindromic sites in which a G⋅C base pair has replaced a T⋅A base pair in each half site (mismatch template) upstream of the core promoter. The concentrations of 3 used were 0 (basal), 10 nM, 100 nM, and 500 nM.