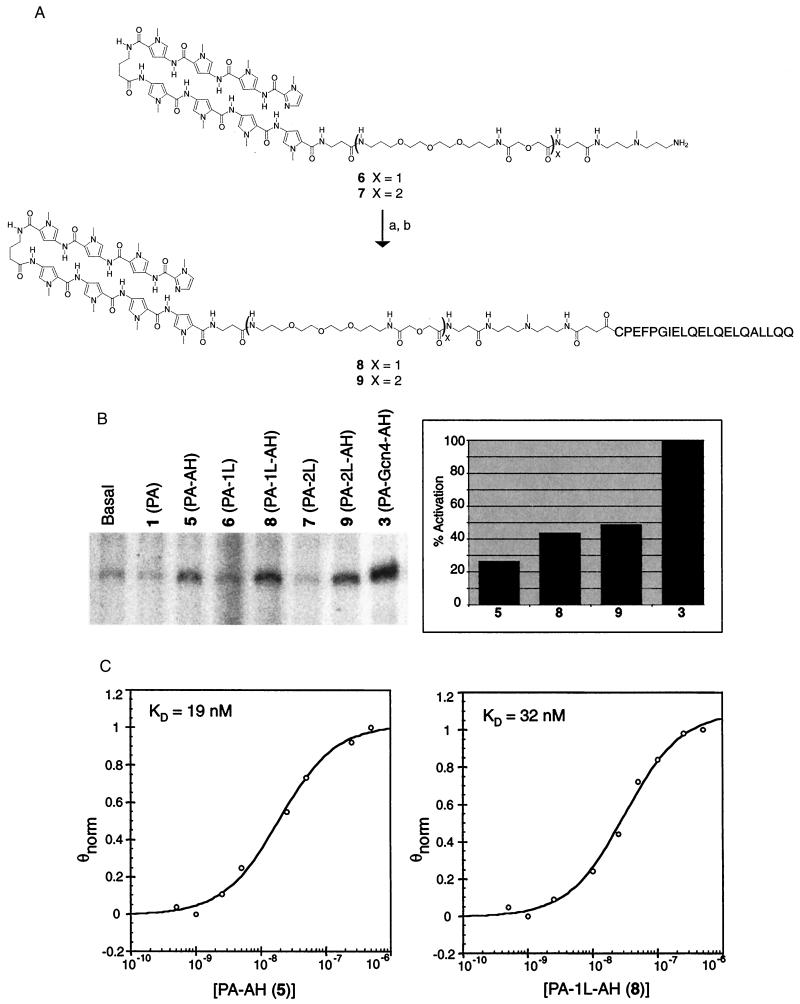
Figure 4.
Substitution of the dimerization module with a flexible ethylene glycol-derived linker. (A) The synthesis of hairpin polyamides 6 and 7 and conjugates 8 and 9 was carried out as described in Fig. 1B. (B) (Left) Storage phosphor autoradiogram showing in vitro transcription reactions containing parent hairpin polyamides 1 (lane 2), 6 (lane 4), and 7 (lane 6) or conjugates 5 (lane 3), 8 (lane 5), and 9 (lane 7), which have the AH peptide attached by flexible linkers of increasing length at 500 nM concentration. A higher conjugate concentration relative to the experiments presented in Figs. 2 and 3 was used to accommodate the slightly lower binding affinity (2- to 3-fold) of conjugates 5, 8, and 9 relative to conjugate 3 (PA-Gcn4-AH). (Right) The activation levels for conjugates 3, 5, 8, and 9 were determined by comparison with the amount of transcript obtained from reactions containing the relevant parent hairpin polyamides. The fold activation values thus obtained are displayed as percentages relative to the fold activation mediated by conjugate 3, defined as 100%. (C) Data from DNase I footprinting titrations with 5 and 8. The curve through each data set is the best-fit Langmuir binding titration isotherm (n = 1) obtained from a nonlinear least-squares algorithm.