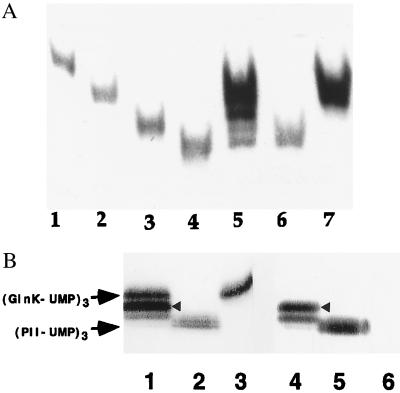
Figure 3.
(A) Formation of PII and GlnK heterotrimers in wild-type E. coli grown in “nitrogen-poor” medium. Western blot of nondenaturing gels of cell extracts detected with monoclonal PII antibody 19G4. Lanes: 1, 2, 3, and 4, purified homotrimeric proteins (GlnK)3, (GlnK-UMP)3, (PII)3, and (PII-UMP)3, respectively; 5, wild type-strain YMC10 (wt); 6, in-frame glnK deletion strain WCH30 (glnK−); 7, glnB deletion strain RB9060 (glnB−); 5–7, cells grown in minimal medium containing glutamine as nitrogen-source. (B) Detection of heterotrimers in wild-type cells grown in arginine medium using monoclonal PII antibody 19G4 (cross reacts with GlnK) (lanes 1–3) and PII monoclonal antibody 24H2 (lanes 4–6), which does not cross-react with GlnK or its uridylylated forms. Lanes: 1 and 4, strain YMC10; 2 and 5, strain WCH30; 3 and 6, strain RB9060. The different intensity of detection of second upper band in lanes 1 and 4 (highlighted with arrowhead) suggests that the identity of that band is most probably (GlnK-UMP)2/PII-UMP (see text). There is almost no PII-UMP homotrimer detected by 19G4 in lane 1 or lane 4, thus suggesting that proportions of homotrimers and heterotrimers vary according to the N source (arginine is a poorer source of N than glutamine).