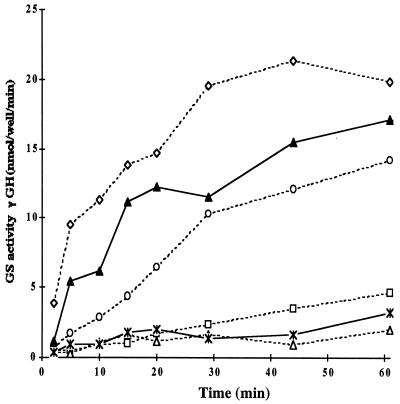
Figure 5.
Uridylylated PII/GlnK heterotrimers can regulate ATase in vitro. The in vitro assay that monitors the rate of formation of γ-glutamyl hydroxamate (γ-GH) based on the γ-glutamyl transferase activity of non-adenylylated GS was used to monitor the effect of heterotrimers on ATase to deadenylylate GS-AMP and was carried out as described (26). The reaction mixture contained Hepes-HCl (100 mM, pH 7.6), BSA (2 mg/ml), potassium phosphate (50 mM), MgCl2 (10 mM), ATP (2 mM, pH 7.2), ATase (27 nM), 2-oxoglutartae (40 mM), GS-AMP (100 nM; n = 11), and PII-UMP, GlnK-UMP, or uridylylated heterotrimers as indicated. Deadenylylation stimulation by untreated PII-UMP (broken line) at 27 nM (open diamond); 6.75 nM (open circle); 1.35 nM (open square); and without PII-UMP (open triangle) are shown. The deadenylylation stimulation by 27 nM of treated mixtures (solid line) of PII-UMP/GlnK-UMP at 1:1 ratio (closed triangle) is presented. Based on proportions of homotrimer PII-UMP in the treated mixtures (see Table 2), it appears that at least the PII-UMP in heterotrimers are active in deadenylylation. Twenty-seven nanomolar purified untreated GlnK-UMP (asterisk connected by solid line) is almost inactive in the deadenylylation assay.