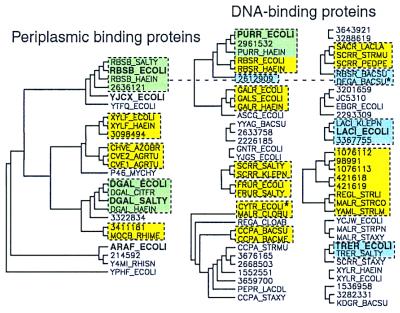
Figure 2.
Three methods for predicting groups of functionally related sequences, applied to the LacI/RbsB family. Significant clusters from a phylogenetic tree of the LacI/RbsB family, created from the final whole-domain multiple alignment by using phylip (see Methods), are indicated with black solid lines. Tree roots not present in ≥30% of the bootstrap replicates were removed. Known PBPs fall into one significant phylogenetic cluster (Left). The remaining sequences are likely to be effector-binding domains of DNA-binding proteins. Proteins are labeled with Swiss-Prot or GenBank accession numbers and with boldface type for solved PDB structures. The bound ligands are the following: RBSB, ribose; YJCX, allose; DGAL, glucose/galactose; ARAF, arabinose; PURR, guanine; LACI, IPTG; TRER, trehalose. The second clustering method is indicated by yellow boxes. These sequence groups were present in ≥30% of bootstrap replicates for the subalignment of ligand-binding residues. A third method of function prediction is indicated by blue boxes; these are sequences whose aligned binding-site residues are capable of matching the ligand-binding interactions of a known structure. Green shading indicates overlap between yellow and blue groups. Only one cluster, the binding-site matches to E. coli RBSB_ECOLI, includes both DNA-binding proteins and PBPs, indicated by a connecting dotted line. Asterisks identify sequences that did not fall into a significant cluster in the whole-domain phylogeny but that belong to a significant cluster using one of the other two methods.