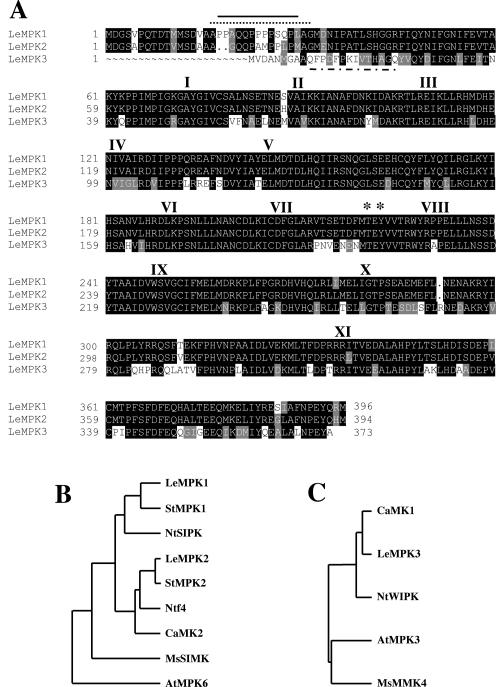
Figure 4.
Amino acid sequence of three L. esculentum MAPKs. A, The deduced amino acid sequences of LeMPKs 1, 2, and 3 were aligned. Identical and conserved amino acids are shaded in black and gray, respectively. Dots represent gaps. Roman numerals represent the 11 conserved kinase subdomains. Asterisks show the Thr and Tyr residues in the TEY phosphorylation motif. The solid line, the dotted line, and the dashed line represent the sequences used as antigenic peptides to generate specific antibodies against LeMPKs 1, 2, and 3, respectively. B, A phylogenetic tree shows the relationship among the A2 group of plant MAPKs (Ichimura et al., 2002). C, A phylogenetic tree shows the relationship among the A1 group of plant MAPK (Ichimura et al., 2002). The tree was created by the GrowTree method from the GCG Wisconsin Package. Accession numbers: StMPK1, AB062138; StMPK2, AB062139; NtSIPK, AAB58396; Ntf4, Q40532; CaMK2, AF247136; MsSIMK, X66469; AtMPK6, S40472; CaMK1, AF247135; NtWIPK, BAA09600; AtMPK3, Q39023; and MsMMK4, X82270.