Figure 3.
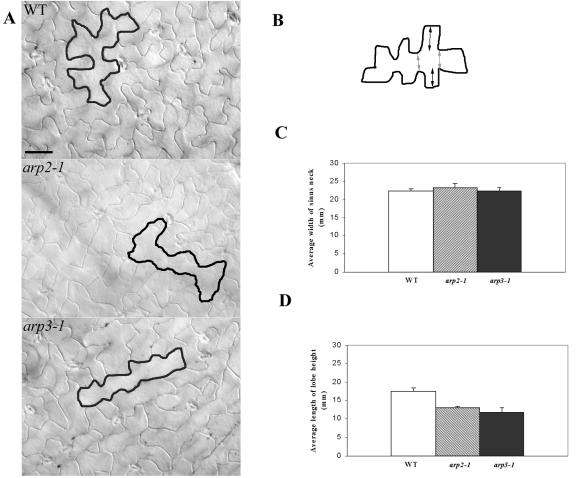
Characterization of leaf pavement cell shapes in arp2-1 and arp3-1 plants. A, Leaf pavement cell shapes. The fourth rosette leaves from 2-week-old plants were cleared, and differential interference contrast images were taken from the middle region of the cleared leaves. Leaves from WT plants and all mutant plants are of similar sizes. Tracing was used to highlight the cell shape of a typical pavement cell. Bars = 30 μm. B, A schematic diagram of a leaf pavement cell illustrates how the lobe height and neck width were measured as shown in C and D. The distance indicated by dark arrows represents the lobe height. The distance indicated by light arrows represents neck width. C, Comparison of the average width of the neck region between WT and mutant pavement cells. Measurements in both C and D were carried out using the fourth leaf of a 2-week-old plant, and 150 epidermal cells were used for each mutant line as well as WT. Statistical test (t test) shows no significant difference in neck width between WT and mutant pavement cells. D, Comparison of the average length of lobe heights between WT and mutant pavement cells. Statistical test (t test) shows that the length of lobe height is significantly reduced in the mutant pavement cell compared with the WT pavement cell.